Python FastApi(6):路径参数和数值校验、查询参数模型
与使用Query为查询参数声明更多的校验和元数据的方式相同,你也可以使用Path为路径参数声明相同类型的校验和元数据。
1 路径参数和数值校验
与使用 Query 为查询参数声明更多的校验和元数据的方式相同,你也可以使用 Path 为路径参数声明相同类型的校验和元数据。
1.1 导入 Path
首先,从 fastapi 导入 Path:
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Query1.2 声明元数据
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(
item_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the item to get")],
q: Annotated[str | None, Query(alias="item-query")] = None,
):
results = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results 路径参数总是必需的,因为它必须是路径的一部分。所以,你应该在声明时将其标记为必需参数。然而,即使你使用 None 声明路径参数或设置一个其他默认值也不会有任何影响,它依然会是必需参数。
1.3 按需对参数排序
假设你想要声明一个必需的 str 类型查询参数 q。而且你不需要为该参数声明任何其他内容,所以实际上你并不需要使用 Query。但是你仍然需要使用 Path 来声明路径参数 item_id。
如果你将带有「默认值」的参数放在没有「默认值」的参数之前,Python 将会报错。但是你可以对其重新排序,并将不带默认值的值(查询参数 q)放到最前面。
对 FastAPI 来说这无关紧要。它将通过参数的名称、类型和默认值声明(Query、Path 等)来检测参数,而不在乎参数的顺序。因此,你可以将函数声明为:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(q: str, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get")):
results = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results1.4 按需对参数排序的技巧
如果你想不使用 Query 声明没有默认值的查询参数 q,同时使用 Path 声明路径参数 item_id,并使它们的顺序与上面不同,Python 对此有一些特殊的语法。传递 * 作为函数的第一个参数。
Python 不会对该 * 做任何事情,但是它将知道之后的所有参数都应作为关键字参数(键值对),也被称为 kwargs,来调用。即使它们没有默认值。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(*, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get"), q: str):
results = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results1.5 数值校验
1.5.1 大于等于
使用 Query 和 Path(以及你将在后面看到的其他类)可以声明字符串约束,但也可以声明数值约束。像下面这样,添加 ge=1 后,item_id 将必须是一个大于(greater than)或等于(equal)1 的整数。
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(
*, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get", ge=1), q: str
):1.5.2 大于和小于等于
同样的规则适用于:
gt:大于(greaterthan)le:小于等于(less than orequal)
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(
*,
item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get", gt=0, le=1000),
q: str,
):1.5.3 浮点数、大于和小于
数值校验同样适用于 float 值。能够声明 gt 而不仅仅是 ge 在这个前提下变得重要起来。例如,你可以要求一个值必须大于 0,使它小于 1。因此,0.5 将是有效值。但是 0.0或 0 不是。对于 lt 也是一样的。
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(
*,
item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get", ge=0, le=1000),
q: str,
size: float = Query(gt=0, lt=10.5),
):2 查询参数模型
如果你有一组具有相关性的查询参数,你可以创建一个 Pydantic 模型来声明它们。这将允许你在多个地方去复用模型,并且一次性为所有参数声明验证和元数据。
2.1 使用 Pydantic 模型的查询参数
在一个 Pydantic 模型中声明你需要的查询参数,然后将参数声明为 Query:
from typing import Annotated, Literal
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
app = FastAPI()
class FilterParams(BaseModel):
limit: int = Field(100, gt=0, le=100)
offset: int = Field(0, ge=0)
order_by: Literal["created_at", "updated_at"] = "created_at"
tags: list[str] = []
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(filter_query: Annotated[FilterParams, Query()]):
return filter_query
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("Test:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, reload=True)
FastAPI 将会从请求的查询参数中提取出每个字段的数据,并将其提供给你定义的 Pydantic 模型。
2.2 查看文档
你可以在 /docs 页面的 UI 中查看查询参数:
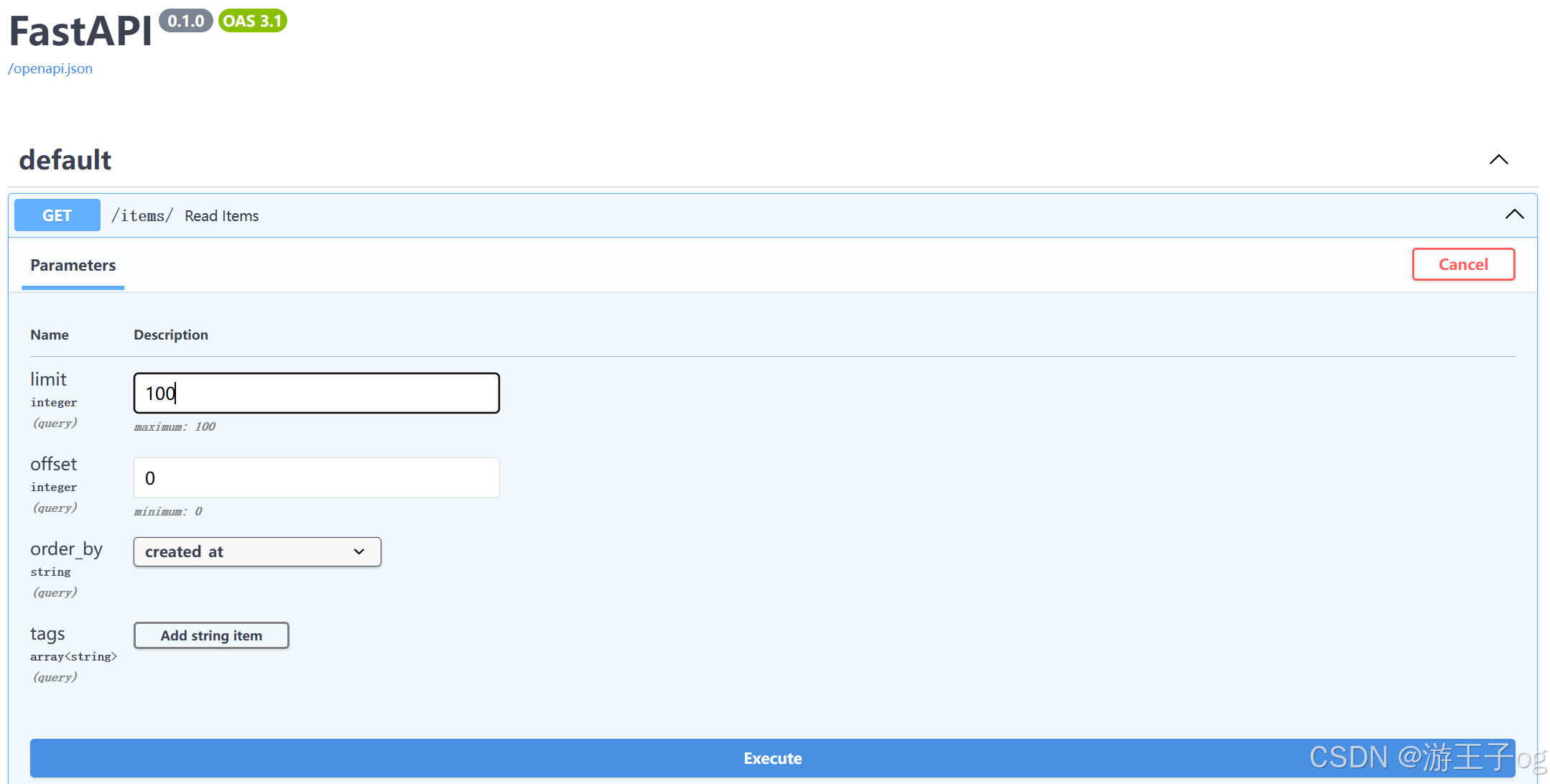
2.3 禁止额外的查询参数
在一些特殊的使用场景中(可能不是很常见),你可能希望限制你要接收的查询参数。你可以使用 Pydantic 的模型配置来设置任何 extra字段:
from typing import Annotated, Literal
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
app = FastAPI()
class FilterParams(BaseModel):
model_config = {"extra": "forbid"}
limit: int = Field(100, gt=0, le=100)
offset: int = Field(0, ge=0)
order_by: Literal["created_at", "updated_at"] = "created_at"
tags: list[str] = []
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(filter_query: Annotated[FilterParams, Query()]):
return filter_query
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run("Test:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, reload=True)
假设有一个客户端尝试在查询参数中发送一些额外的数据,它将会收到一个错误响应。例如,如果客户端尝试发送一个值为 plumbus 的 tool 查询参数,如:
https://example.com/items/?limit=10&tool=plumbus 他们将收到一个错误响应,告诉他们查询参数 tool 是不允许的:
{
"detail": [
{
"type": "extra_forbidden",
"loc": ["query", "tool"],
"msg": "Extra inputs are not permitted",
"input": "plumbus"
}
]
}
GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容









所有评论(0)