52,Python数分之Pandas训练,力扣,1294. 不同国家的天气类型
Python数分之Pandas训练 不同方法和详细思路与步骤 解:力扣,1294. 不同国家的天气类型
·
- 学习:知识的初次邂逅
- 复习:知识的温故知新
- 练习:知识的实践应用
目录
一,原题力扣链接
二,题干
表:
Countries+---------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +---------------+---------+ | country_id | int | | country_name | varchar | +---------------+---------+ country_id 是这张表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。 该表的每行有 country_id 和 country_name 两列。表:
Weather+---------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +---------------+---------+ | country_id | int | | weather_state | varchar | | day | date | +---------------+---------+ (country_id, day) 是该表的复合主键(具有唯一值的列)。 该表的每一行记录了某个国家某一天的天气情况。编写解决方案找到表中每个国家在 2019 年 11 月的天气类型。
天气类型的定义如下:
- 当
weather_state的平均值小于或等于15返回 Cold,- 当
weather_state的平均值大于或等于25返回 Hot,- 否则返回 Warm。
以 任意顺序 返回你的查询结果。
返回结果格式如下所示:
示例 1:
输入: Countries table: +------------+--------------+ | country_id | country_name | +------------+--------------+ | 2 | USA | | 3 | Australia | | 7 | Peru | | 5 | China | | 8 | Morocco | | 9 | Spain | +------------+--------------+ Weather table: +------------+---------------+------------+ | country_id | weather_state | day | +------------+---------------+------------+ | 2 | 15 | 2019-11-01 | | 2 | 12 | 2019-10-28 | | 2 | 12 | 2019-10-27 | | 3 | -2 | 2019-11-10 | | 3 | 0 | 2019-11-11 | | 3 | 3 | 2019-11-12 | | 5 | 16 | 2019-11-07 | | 5 | 18 | 2019-11-09 | | 5 | 21 | 2019-11-23 | | 7 | 25 | 2019-11-28 | | 7 | 22 | 2019-12-01 | | 7 | 20 | 2019-12-02 | | 8 | 25 | 2019-11-05 | | 8 | 27 | 2019-11-15 | | 8 | 31 | 2019-11-25 | | 9 | 7 | 2019-10-23 | | 9 | 3 | 2019-12-23 | +------------+---------------+------------+ 输出: +--------------+--------------+ | country_name | weather_type | +--------------+--------------+ | USA | Cold | | Austraila | Cold | | Peru | Hot | | China | Warm | | Morocco | Hot | +--------------+--------------+ 解释: USA 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (15) / 1 = 15 所以天气类型为 Cold。 Australia 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (-2 + 0 + 3) / 3 = 0.333 所以天气类型为 Cold。 Peru 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (25) / 1 = 25 所以天气类型为 Hot。 China 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (16 + 18 + 21) / 3 = 18.333 所以天气类型为 Warm。 Morocco 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (25 + 27 + 31) / 3 = 27.667 所以天气类型为 Hot。 我们并不知道 Spain 在 11 月的 weather_state 情况所以无需将他包含在结果中。
三,建表语句
import pandas as pd
data = [[2, 'USA'], [3, 'Australia'], [7, 'Peru'], [5, 'China'], [8, 'Morocco'], [9, 'Spain']]
countries = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['country_id', 'country_name']).astype({'country_id':'Int64', 'country_name':'object'})
data = [[2, 15, '2019-11-01'], [2, 12, '2019-10-28'], [2, 12, '2019-10-27'], [3, -2, '2019-11-10'], [3, 0, '2019-11-11'], [3, 3, '2019-11-12'], [5, 16, '2019-11-07'], [5, 18, '2019-11-09'], [5, 21, '2019-11-23'], [7, 25, '2019-11-28'], [7, 22, '2019-12-01'], [7, 20, '2019-12-02'], [8, 25, '2019-11-05'], [8, 27, '2019-11-15'], [8, 31, '2019-11-25'], [9, 7, '2019-10-23'], [9, 3, '2019-12-23']]
weather = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['country_id', 'weather_state', 'day']).astype({'country_id':'Int64', 'weather_state':'Int64', 'day':'datetime64[ns]'})四,分析
思路
表格大法:
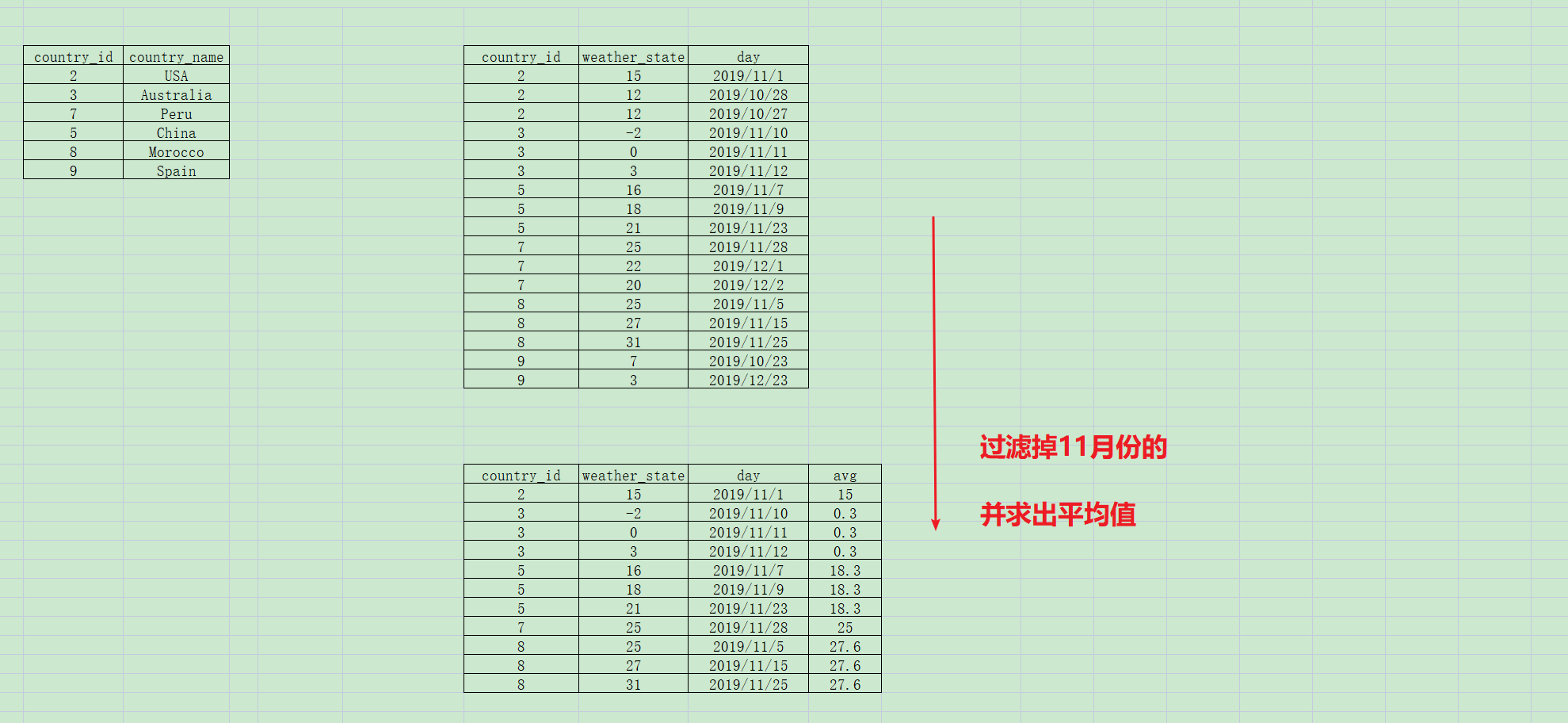
第一步,过滤11月份的数据,
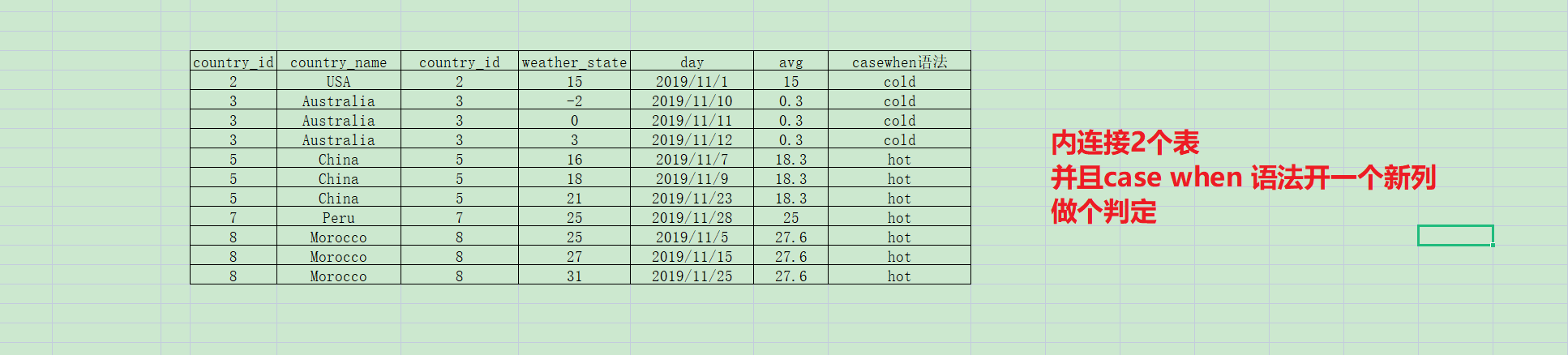
第二步,内连接2个表,条件是国家id=国家id
第三步:以国家id,国家姓名分组,求出每个国家11月份的平均天气
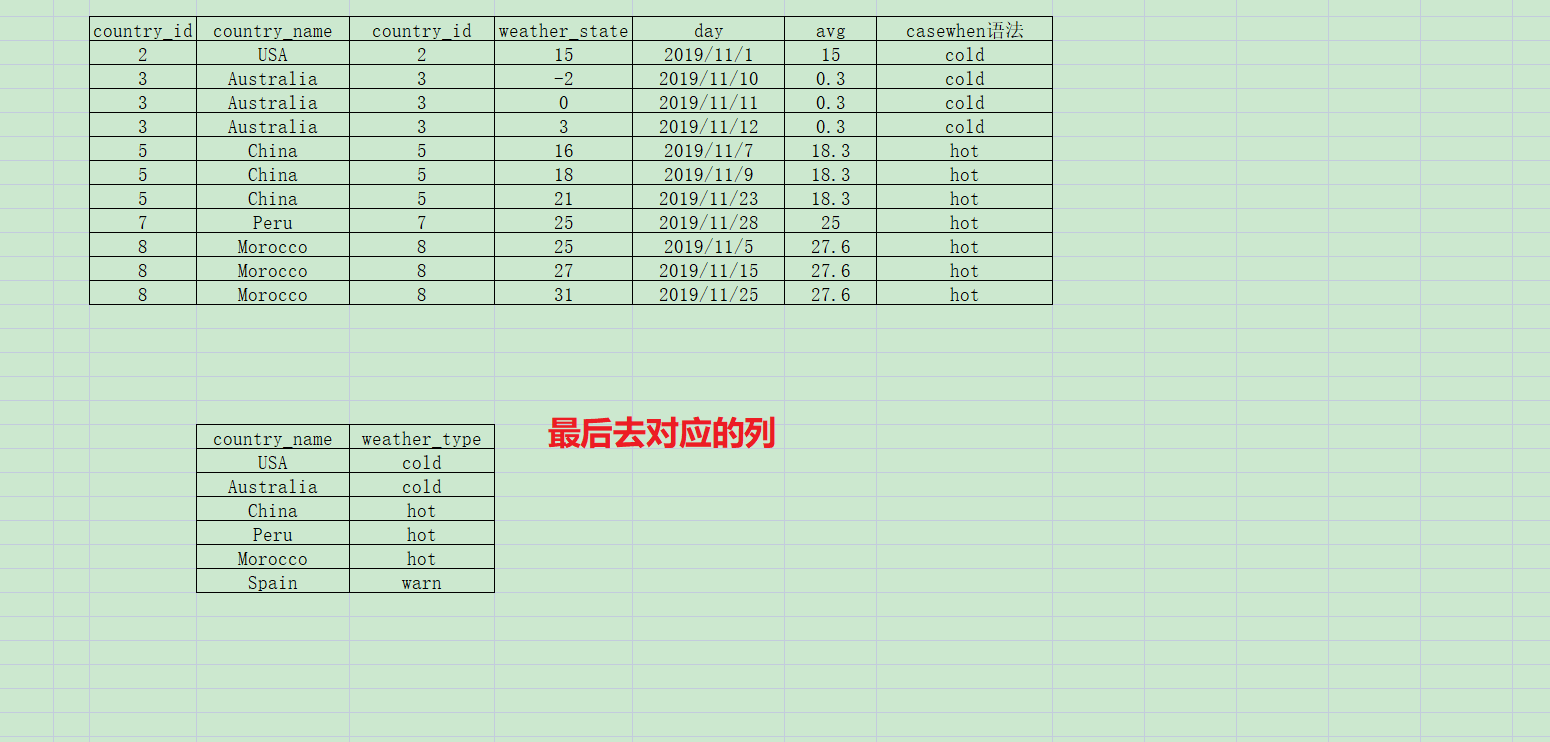
第四步:针对平均天气case when语法 或者pandas中自定义函数的方式开一个新列 赋对应的值
第五步:映射指定的列,并输出
解题过程
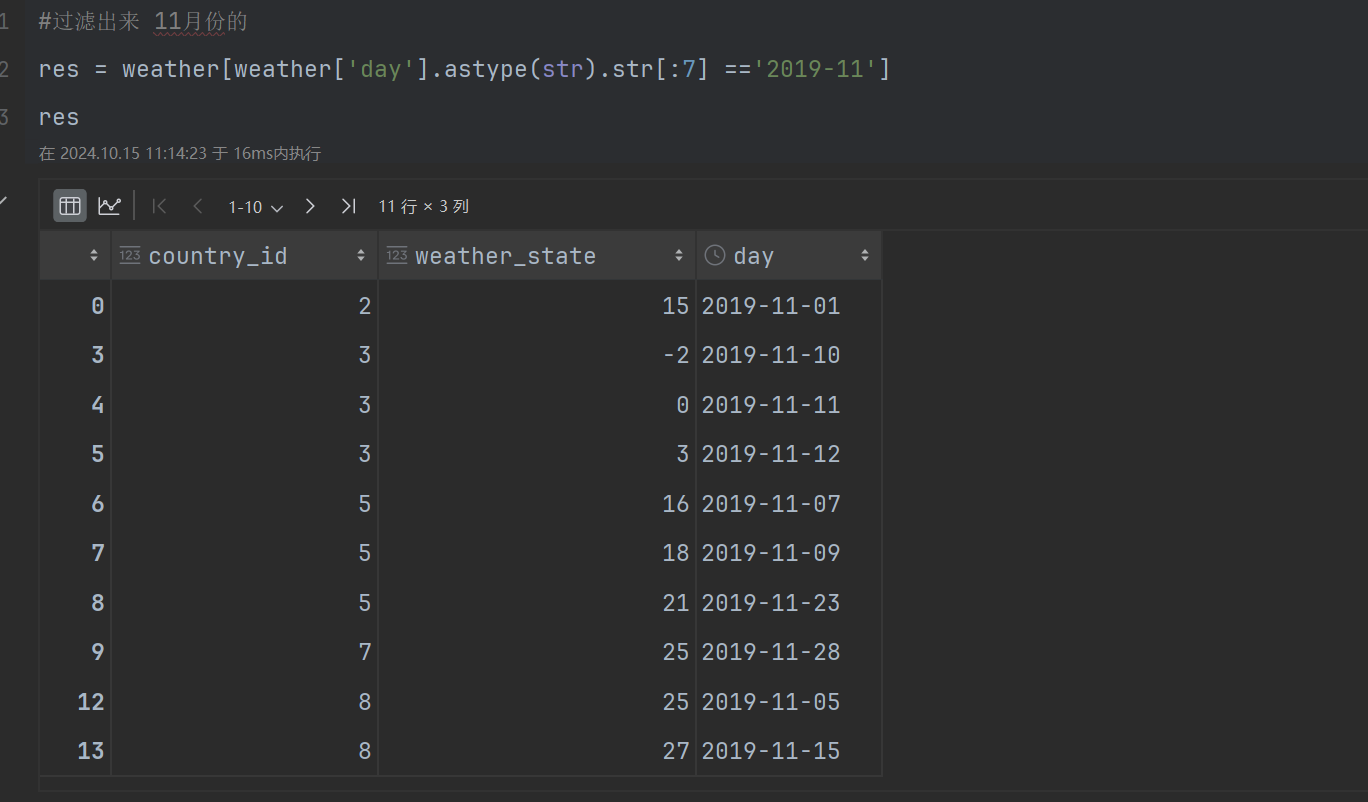
第一步,过滤11月份的数据,
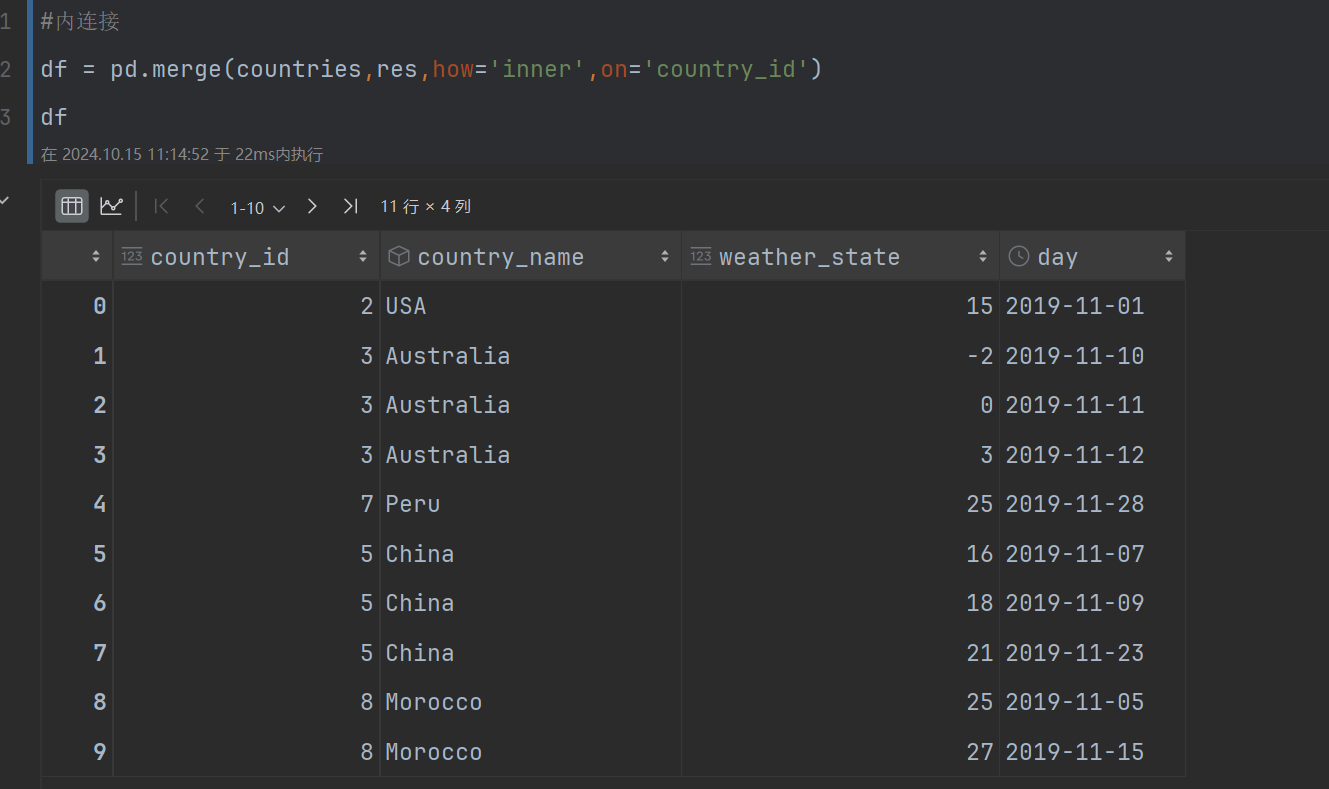
在pandas 第二步,内连接2个表,条件是国家id=国家id
在pandas
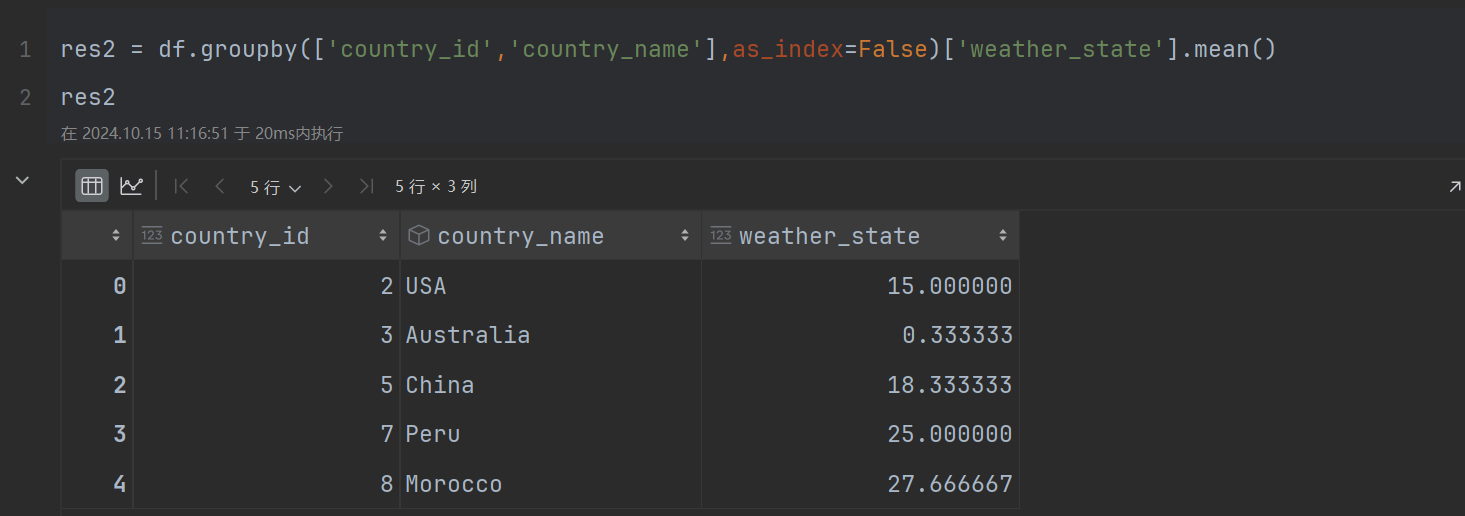
第三步:以国家id,国家姓名分组,求出每个国家11月份的平均天气
在pandas
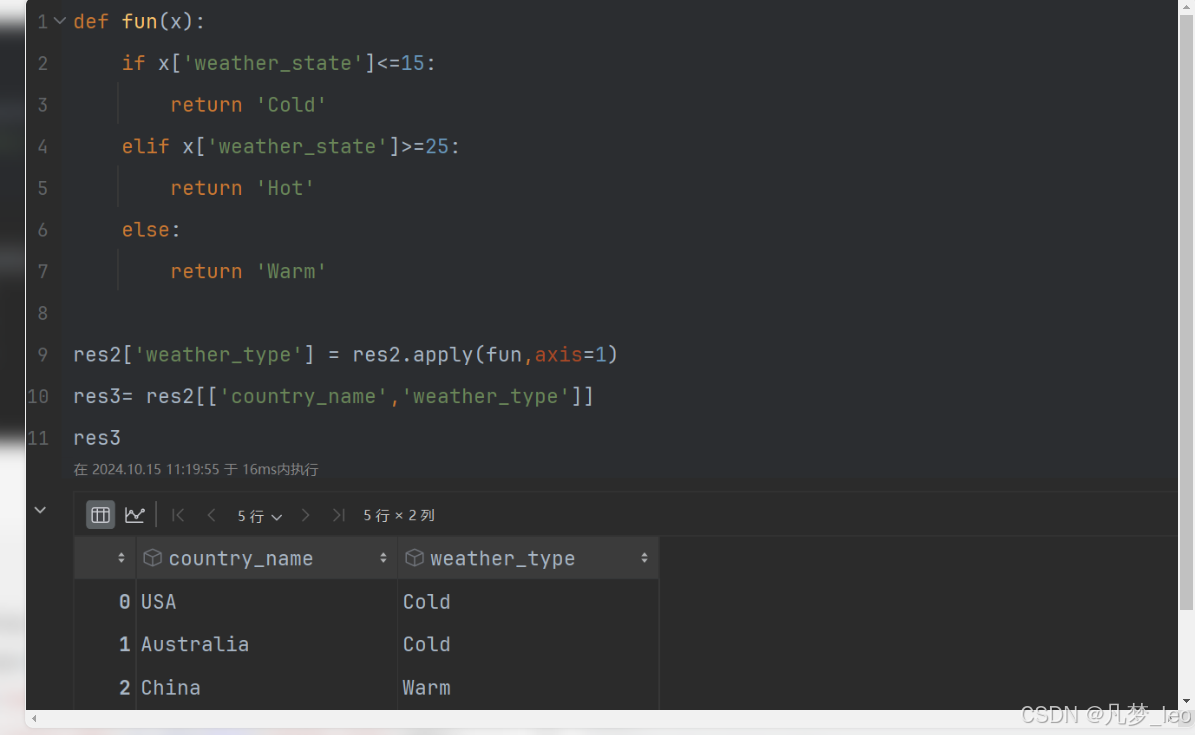
第四步:针对平均天气case when语法 或者pandas中自定义函数的方式开一个新列 赋对应的值
在pandas
第五步:映射指定的列,并输出
在pandas
五,Pandas解答
import pandas as pd
def weather_type(countries: pd.DataFrame, weather: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
#过滤出来 11月份的
res = weather[weather['day'].astype(str).str[:7] =='2019-11']
#内连接
df = pd.merge(countries,res,how='inner',on='country_id')
#分组聚合
res2 = df.groupby(['country_id','country_name'],as_index=False)['weather_state'].mean()
#自定义函数 模拟sql中casewhen效果
def fun(x):
if x['weather_state']<=15:
return 'Cold'
elif x['weather_state']>=25:
return 'Hot'
else:
return 'Warm'
res2['weather_type'] = res2.apply(fun,axis=1)
res3= res2[['country_name','weather_type']]
return res3
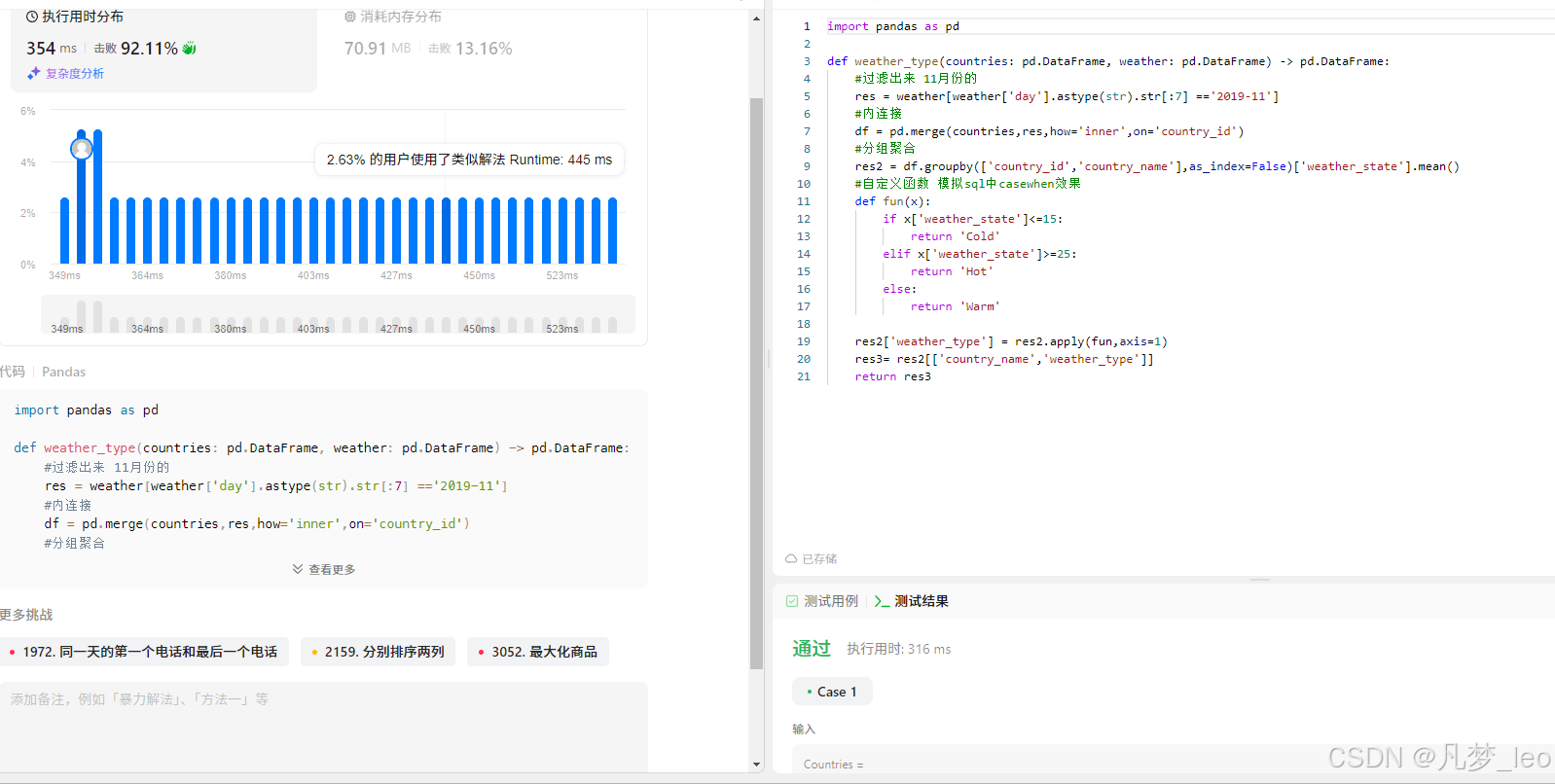
weather_type(countries,weather)六,验证
七,知识点总结
- Pandas中对时间列截取的运用
- Pandas中内连接的运用
- Pandas中分组聚合并且重置索引的运用
- Pandas中自定义函数的运用
- Pandas中映射指定的列的运用
- Python选择分支的运用
- Python条件过滤的运用
- Python中函数的运用
- 学习:知识的初次邂逅
- 复习:知识的温故知新
- 练习:知识的实践应用

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容









所有评论(0)