仅需10道题轻松掌握Python文件处理 Python技能树征题
先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新大数据全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵
先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7
深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新大数据全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。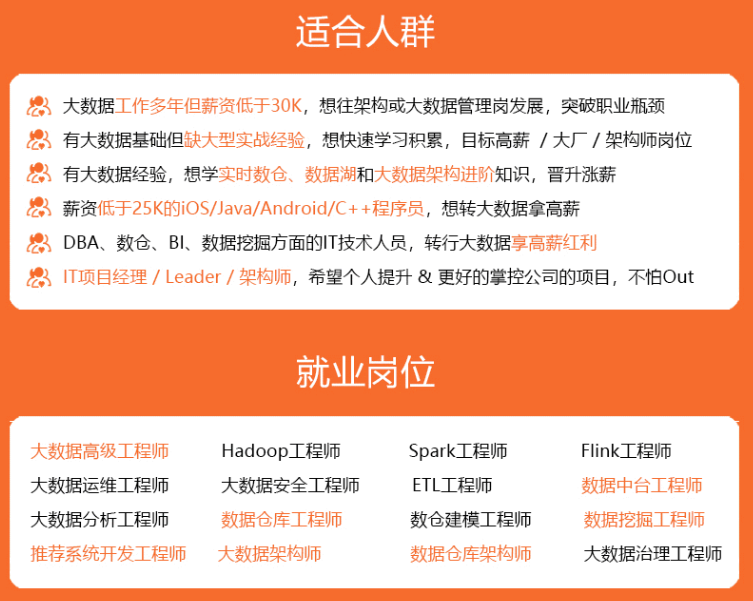
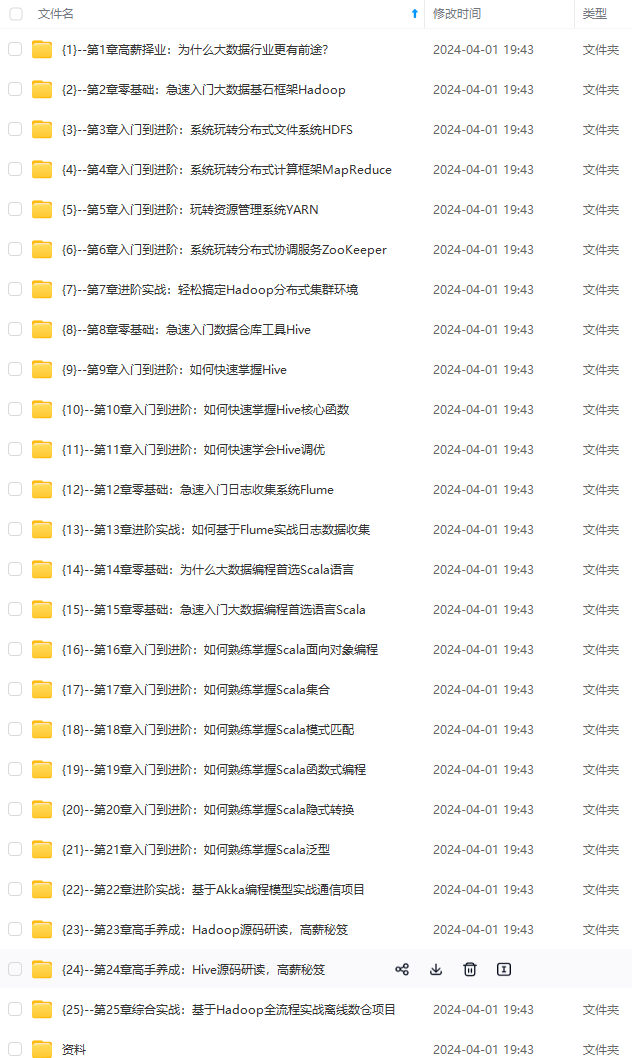
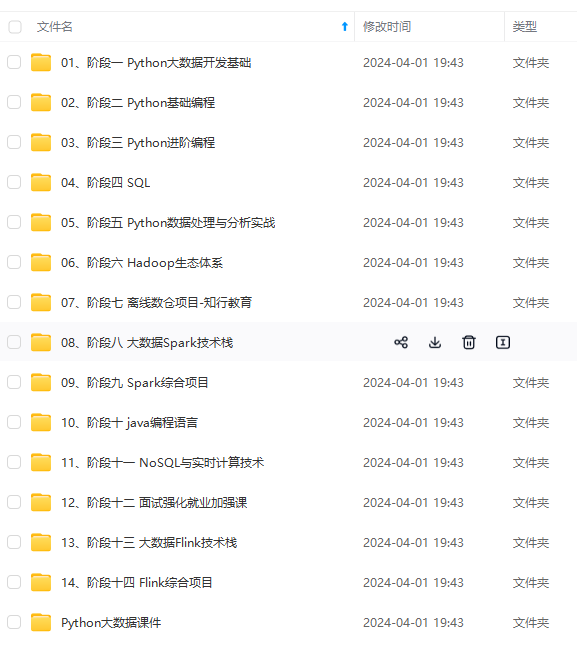
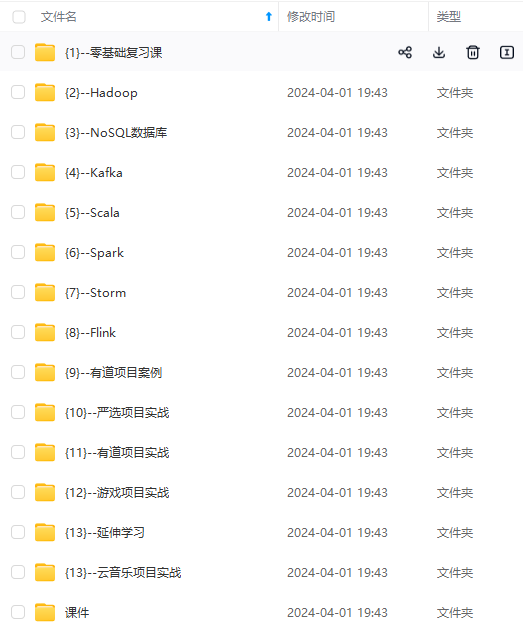
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你需要这些资料,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注大数据)
正文
B.
import os
exist = os.path.isdir(‘etc/passwd’)
print(exist)
C.
import os
exist = os.path.isdir(‘/etc/passwd’)
print(exist)
D.
import os
exist = os.path.isfile(‘/etc/passwd’)
print(exist)
正确答案: D
### 3. 第 3 题:获取指定文件夹下的文件列表
知识点描述:获取文件系统中指定目录下的所有文件列表。
问题描述:获取 “/etc” 目录中所有 python 文件(以 “.py” 作为文件后缀)列表,请从以下选项中选出你认为正确的选项:
A.
import os
path = “/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages”
names = [name for name in os.listdir(path)]
print(names)
B.
import os
path = “/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages”
names = [name for name in os.listdir(path) if name.endswith(‘.py’)]
print(names)
C.
import os
path = “/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages”
names = [name for name in os.listdir(path) if os.path.isfile(name) and name.endswith(‘.py’)]
print(names)
D.
import os
path = “/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages”
names = [name for name in os.listdir(path) if name.endswith(‘*.py’)]
print(names)
正确答案: B
### 4. 第 4 题:文本文件的读写
知识点描述:读写使用不同编码方式的文本文件。
问题描述:假设存在一文件 “text\_1.txt”,如何向其中再添加两行新数据,请从以下选项中选出你认为正确的选项:
A.
new_line_1 = “New line 1”
new_line_2 = “New line 2”
with open(‘text_1.txt’, ‘rt’) as f:
f.write(new_line_1+‘\n’)
f.write(new_line_2+‘\n’)
B.
new_line_1 = “New line 1”
new_line_2 = “New line 2”
with open(‘text_1.txt’, ‘at’) as f:
f.write(new_line_1)
f.write(new_line_2)
C.
new_line_1 = “New line 1”
new_line_2 = “New line 2”
with open(‘text_1.txt’, ‘wt’) as f:
f.write(new_line_1+‘\n’)
f.write(new_line_2+‘\n’)
D.
new_line_1 = “New line 1”
new_line_2 = “New line 2”
with open(‘text_1.txt’, ‘at’) as f:
f.write(new_line_1+‘\n’)
f.write(new_line_2+‘\n’)
正确答案: D
### 5. 第 5 题:将打印输出到文件中
知识点描述:将 print() 函数的输出重定向到指定日志文件中。
问题描述:将当前时间写入日志文件 “log.txt” 中,并记录函数执行结果,请从以下选项中选出你认为正确的答案:
A.
from datetime import datetime
def hello_world(num):
return “Hello world {}!”.format(num)
for i in range(10):
with open(‘log.txt’, ‘at’) as f:
print(str(datetime.today()) + ‘\t’ + hello_world(i), file=f)
B.
from datetime import datetime
def hello_world(num):
return “Hello world {}!”.format(num)
for i in range(10):
with open(‘log.txt’, ‘at’) as f:
print(datetime.today() + ‘\t’ + hello_world(i), file=f)
C.
from datetime import datetime
def hello_world(num):
return “Hello world {}!”.format(num)
for i in range(10):
with open(‘log.txt’, ‘wt’) as f:
print(datetime.today() + ‘\t’ + hello_world(i))
D.
from datetime import datetime
def hello_world(num):
return “Hello world {}!”.format(num)
for i in range(10):
with open(‘log.txt’, ‘wt’) as f:
print(str(datetime.today()) + ‘\t’ + hello_world(i), file=f)
正确答案: A
### 6. 第 6 题:二进制文件的读写
知识点描述:读写二进制文件,如图片、声音文件等。
问题描述:已知存在二进制文件 “test.bin”,如何正确向此文件追加写入文本数据,请从以下选项中选出你认为正确的答案:
A.
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘at’) as f:
text = ‘Hello World!\n’
f.write(text)
B.
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘wb’) as f:
text = ‘Hello World!\n’
f.write(text.encode(‘utf-8’))
C.
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘ab’) as f:
text = ‘Hello World!\n’
f.write(text.encode(‘utf-8’))
D.
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘ab’) as f:
text = ‘Hello World!\n’
f.write(text)
正确答案: C
### 7. 第 7 题:压缩文件的读写
知识点描述:读写 gzip 或 bz2 格式的压缩文件。
问题描述:请从以下选项中选择能够将文本文件 “text.txt” 内容写入压缩文件 “compress.gz” 的程序,且要求压缩程度最佳:
A.
import gzip
text = ‘text.txt’
with gzip.open(‘compress.gz’, ‘wt’, compresslevel = 9) as f:
f.write(text)
B.
import gzip
text = ‘text.txt’
with gzip.open(‘compress.gz’, ‘wt’, compresslevel = 0) as f:
f.write(text)
C.
import gzip
text = ‘text.txt’
with open(text, ‘rt’) as file:
read_text = file.read()
with gzip.open(‘compress.gz’, ‘wt’, compresslevel = 9) as f:
f.write(read_text)
D.
import gzip
text = ‘text.txt’
with open(text, ‘rt’) as file:
read_text = file.read()
with gzip.open(‘compress.gz’, ‘wt’, compresslevel = 0) as f:
f.write(read_text)
正确答案:C
### 8. 第 8 题:以固定数据块大小读取文件
知识点描述:以固定长度数据块长度迭代读取文件,而非逐行读取。
问题描述:存在一文件 “test.bin”,编写程序每次读取数据块大小为 16B,直到文件末尾:
A.
from functools import partial
RECORD_SIZE = 16
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘rt’) as f:
records = iter(partial(f.read, RECORD_SIZE), b’')
for r in records:
print®
B.
from functools import partial
RECORD_SIZE = 16
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘rb’) as f:
records = iter(partial(f.read, RECORD_SIZE), b’')
for r in records:
print®
C.
from functools import partial
RECORD_SIZE = 16 * 8
with open(‘test.bin’, ‘rt’) as f:
records = iter(partial(f.read, RECORD_SIZE), b’')
for r in records:
print®
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注大数据)**

**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
\* 8
with open('test.bin', 'rt') as f:
records = iter(partial(f.read, RECORD_SIZE), b'')
for r in records:
print(r)
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注大数据)
[外链图片转存中…(img-AkQ0BphZ-1713373281374)]
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)