Ascend的aclgraph(十)另外一种成图方式GeConcreteGraph
您可以在调用该接口后,调用GetCompiledGraphSummary获取图编译结果的概要信息(比如模型执行所需的内存资源大小及内存是否可刷新、复用等),根据查询到的内存大小,自行申请并管理内存;您可以配合编译后Graph资源占用查询接口、内存的基地址刷新接口来使用,达到自行管理模型内存、获得更多灵活性的目的。ge中涉及到的代码页比较复杂,本篇还是关注ge图与torch.compile对接,不深
1 回顾
在Ascend的aclgraph(一)aclgraph是什么?torchair又是怎么成图的?中提到了GeConcreteGraph的概念,
if self.config.mode.value == "max-autotune":
from torchair._ge_concrete_graph.fx2ge_converter import GeConcreteGraph
graph = GeConcreteGraph(self.config, name="graph_" + str(_next_unique_graph_id()))
elif self.config.mode.value == "reduce-overhead":
from torchair._acl_concrete_graph.fx2acl_converter import AclConcreteGraph
graph = AclConcreteGraph(self.config)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported npu backend mode: {self.config.mode.value}.")
AclConcreteGraph已经介绍完了,此篇对GeConcreteGraph进行分析了解下。
2 GeConcreteGraph
先给出代码中定义(部分片段)
class GeConcreteGraph(ConcreteGraphBase):
def __init__(self, config: CompilerConfig, name=None):
self._graph = GeGraph(name=name)
self._fx_outputs = []
self._fx_outputs_mapping = dict()
self._outputs = []
self._fx_input_names = []
self._input_process = None
self._input_info_list = []
self._graph_output_ref_input = {}
self._ref_data_idx = []
self._cloned_ge_input_mapping = {}
self._config = config
self._auto_tune_times = 0
self._converter_ctx = threading.local()
self._is_compiled = False
self._all_sym_input_idx = {}
self._all_meta_tensor_input = {}
self._fx_graph = None
重点关注self._graph,它是个GeGraph对象,
2.1 GeGraph
先看GeGraph的定义
class GeGraph(object):
def __init__(self, model_def=None, serialized_model_def=None, name=None):
from torchair.core._backend import TorchNpuGraph
if model_def is not None and serialized_model_def is not None:
raise AssertionError(f"Unsupported init method: both model_def and serialized_model_def are specified.")
elif model_def is None and serialized_model_def is None:
self._model = ModelDef()
self._proto = self._model.graph.add()
elif serialized_model_def is not None:
self._model = ModelDef()
self._model.ParseFromString(serialized_model_def)
self._proto = self._model.graph[0]
else:
self._model = model_def
self._proto = self._model.graph[0]
self._proto.name = name if name is not None else self._proto.name
self._executor = TorchNpuGraph(self._proto.name)
self._python_code = self._python_code_init()
self._generator_rng_state = defaultdict(map_graph_rng_state)
self._indexed_inputs = {}
self._named_inputs_info = {}
self._used_process_group = {}
self._dont_prune_me_ops = []
根据GeGraph只传入了name可知,走的是
self._model = ModelDef()
self._proto = self._model.graph.add()
其中ModelDef的定义是
ModelDef = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ModelDef', (_message.Message,), {
'AttrEntry': _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('AttrEntry', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR': _MODELDEF_ATTRENTRY,
'__module__': 'ge_ir_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:ge.proto.ModelDef.AttrEntry)
}),
'DESCRIPTOR': _MODELDEF,
'__module__': 'ge_ir_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:ge.proto.ModelDef)
})
这段代码通过使用 Protocol Buffers 的反射机制,动态地创建了两个消息类型:ModelDef 和其内部的嵌套消息类型 AttrEntry。这些消息类型通常会在 .proto 文件中定义,并由 Protocol Buffers 编译器生成相应的 Python 代码。
2.2 TorchNpuGraph
上述代码中,还引入了TorchNpuGraph的概念。
self._executor = TorchNpuGraph(self._proto.name)
TorchNpuGraph的定义如下
class TorchNpuGraph(_torchair.TorchNpuGraphBase):
def __init__(self, name=""):
super(TorchNpuGraph, self).__init__(str(name))
@pretty_error_msg
def load(self, ge_graph, options=None):
"""Load the graph"""
options = {} if options is None else options
input_placements = ge_graph.attr["_input_placements"].list.i
output_dtypes = ge_graph.attr["_output_dtypes"].list.i
executor_type = ge_graph.attr["_executor_type"].i
inputs_shape = _get_input_shape(ge_graph)
super(TorchNpuGraph, self).load(ge_graph.SerializeToString(), options, input_placements, output_dtypes,
executor_type)
super(TorchNpuGraph, self).set_hint_shape(inputs_shape, [])
logger.debug('Load graph set_hint_shape input shape: %s', inputs_shape)
@pretty_error_msg
def compile(self):
"""Compile the graph"""
return super(TorchNpuGraph, self).compile()
@pretty_error_msg
def auto_tune(self, example_inputs=[], stream=None):
"""Compile the graph with aoe"""
return super(TorchNpuGraph, self).auto_tune((example_inputs, stream))
@pretty_error_msg
def run(self, inputs, assigned_outputs=[], stream=None):
"""Run the graph"""
return super(TorchNpuGraph, self).run((inputs, assigned_outputs, stream))
TorchNpuGraphBase是一个pybind的类型,
py::class_<tng::TorchNpuGraphBase>(m, "TorchNpuGraphBase")
.def(py::init<const std::string &>())
.def("load", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::Load)
.def("set_hint_shape", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::SetHintShape)
.def("compile", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::Compile)
.def("auto_tune", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::AutoTune)
.def("summary", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::Summary)
.def("run", &tng::TorchNpuGraphBase::Run);
提供了compile和run等接口。
2.2 GeConcreteGraph的__call__函数
定义如下,给出关键代码片段
def __call__(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
... 省略 ...
self.update_graph_with_runtime(inputs, args)
... 省略 ...
if not self._is_compiled:
local_compile_options, global_compile_options = self._normalize_ge_option()
initialize_graph_engine(global_compile_options)
self.graph.load(local_compile_options)
if self.should_auto_tune:
self.auto_tune(inputs)
self.compile()
... 省略 ...
首次编译,流程图如下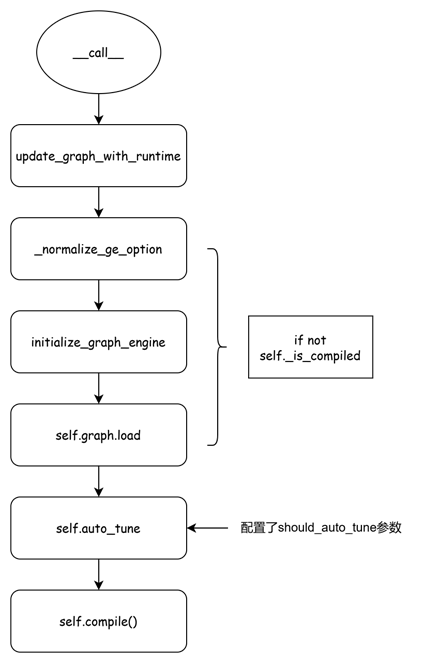
update_graph_with_runtime应该是根据ge图的执行规则,对图的输入进行一些处理。_normalize_ge_option是获取了一些接下来图编译的选项配置。initialize_graph_engine调用InitializeGraphEngine。
def initialize_graph_engine(global_compile_options: Dict = None):
options: Dict[str, str] = {}
options.update(_try_get_global_init_compile_option(global_compile_options))
options['ge.exec.deviceId'] = str(_get_device_id())
options['ge_run_with_torch_npu'] = '1' if 'torch_npu' in sys.modules else '0'
options.update(_get_global_op_compile_config())
_torchair.InitializeGraphEngine(options)
InitializeGraphEngine是一个pybind函数,代码片段如下
Status Session::Initialize(const std::map<std::string, std::string> &options) {
if (initialized_) {
return status_;
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> const lock(mu_);
if (initialized_) {
return status_;
}
... 省略 ...
std::map<ge::AscendString, ge::AscendString> ge_options;
TNG_LOG(INFO) << "Initializing GE with options:";
for (const auto &option : options) {
TNG_LOG(INFO) << " " << option.first << ": " << option.second;
if (option.first == "ge_run_with_torch_npu") {
run_with_torch_npu_ = option.second == "1";
continue;
}
ge_options[option.first.c_str()] = option.second.c_str();
}
... 省略 ...
if (ge::GEInitialize(ge_options) != ge::SUCCESS) {
status_ = Status::Error("Failed to initialize GE %s", compat::GeErrorStatus().GetErrorMessage());
} else {
(void)ge_options.emplace(ge::AscendString("ge.session_device_id"), iter->second);
global_ge_session = std::make_unique<ge::Session>(ge_options);
if (global_ge_session == nullptr) {
status_ = Status::Error("Failed to create GE session");
}
}
auto ret = aclrtSetDevice(device_index_);
TNG_ASSERT(ret == ACL_ERROR_NONE, "ACL set device id failed, return %d", ret);
libge_runner_handle = dlopen("libge_runner.so", RTLD_NOW);
... 省略 ...
主要也就是初始化GE引擎的一些资源,包括stream,device等配置。有关GE的介绍,可以查阅GE图。
关注下self.graph.load(local_compile_options)函数,调用栈如下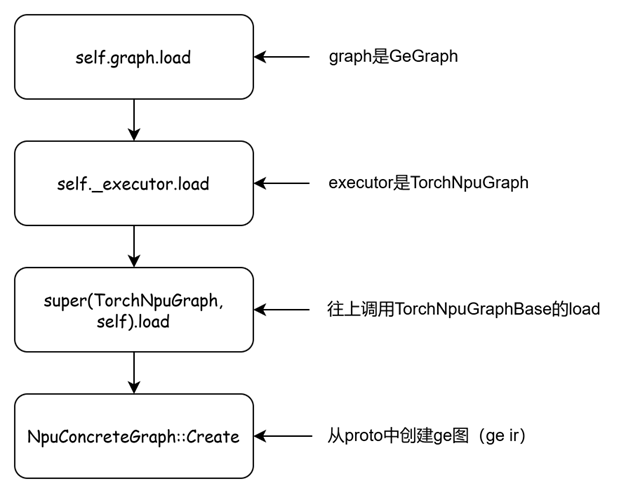
可以看到,执行完成self.graph.load(local_compile_options),ge的图就创建好了。
ge中涉及到的代码页比较复杂,本篇还是关注ge图与torch.compile对接,不深入探讨ge细节。auto_tune也是pybind函数,最终调用的是RunAoeTuning。AOE调优,可以参见昇腾社区
AOE调优工具
2.3 compile
回到GeConcreteGraph的compile部分
def compile(self) -> Any:
if self._is_compiled:
return
logger.info(f'start compile graph: {self.graph.name}.')
self.graph.compile()
self._is_compiled = True
logger.info(f'end compile graph: {self.graph.name} and start run graph.')
接着调用
def compile(self):
self._executor.compile()
_executor是TorchNpuGraph,因此最终还是到TorchNpuGraphBase::Compile()
流程图如下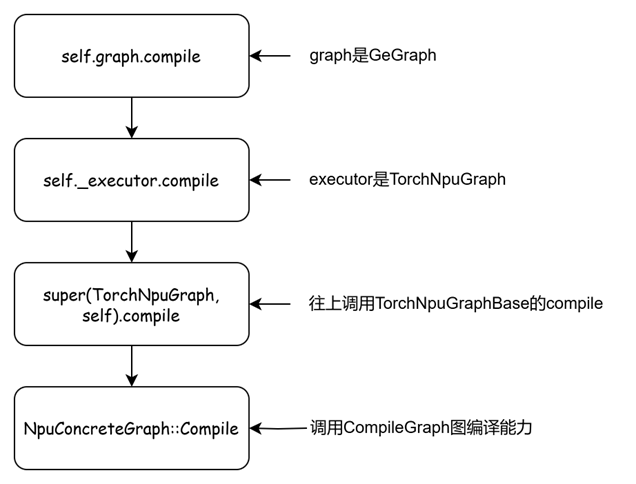
最终是调用到GE的API CompileGraph,根据社区资料https://www.hiascend.com/document/detail/zh/canncommercial/81RC1/apiref/ascendgraphapi/atlasgeapi_07_0103.html给出其解释如下
函数原型
Status CompileGraph(uint32_t graph_id)
参数说明
同步编译指定id对应的Graph图。与BuildGraph相比,该接口仅包含图编译功能,不生成可用于执行的模型,BuildGraph包含了图编译过程,并在编译完成后进行模型所需内存资源的初始化,生成可用于执行的模型。
该接口不包含模型所需内存资源管理功能,而是将这部分管理内存的工作开放给用户。您可以配合编译后Graph资源占用查询接口、内存的基地址刷新接口来使用,达到自行管理模型内存、获得更多灵活性的目的。
您可以在调用该接口后,调用GetCompiledGraphSummary获取图编译结果的概要信息(比如模型执行所需的内存资源大小及内存是否可刷新、复用等),根据查询到的内存大小,自行申请并管理内存;然后通过SetGraphConstMemoryBase、 UpdateGraphFeatureMemoryBase对内存基址进行设置和刷新。
3 e2e执行GeConcreteGraph
同样,给出一个完整的调用例子。
import torch
import torch_npu
import torchair
import logging
from torchair import logger
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
import logging
torch._logging.set_logs(dynamo=logging.DEBUG,aot=logging.DEBUG,output_code=True,graph_code=True)
# Patch方式实现集合通信入图(可选)
from torchair import patch_for_hcom
patch_for_hcom()
# 定义模型Model
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x, y):
return torch.add(x, y)
# 实例化模型model
model = Model().npu()
# 获取TorchAir提供的默认npu backend,自行配置config功能
config = torchair.CompilerConfig()
npu_backend = torchair.get_npu_backend(compiler_config=config)
# 使用npu backend进行compile
opt_model = torch.compile(model, backend=npu_backend)
# 使用编译后的model去执行
x = torch.randn(2, 2).npu()
y = torch.randn(2, 2).npu()
out = opt_model(x, y)
print(out)
get_npu_backend和torch.compile的过程,与Ascend的aclgraph(九)AclConcreteGraph:e2e执行aclgraph是一样的,这里不再赘述。直接关注opt_model运行的时候会发生的事情。
通过Ascend的aclgraph(三)TorchDynamo或者Ascend的aclgraph(九)AclConcreteGraph:e2e执行aclgraph可知,给frame设置了callback函数,该callback函数是convert_frame.convert_frame(backend, hooks=hooks)。
具体看看convert_frame函数的作用就是convert a frame into an FX graph,调用过程如下
def convert_frame(compiler_fn: CompilerFn, hooks: Hooks) -> ConvertFrame:
"""Try to convert a frame into an FX graph, if error leave frame unmodified"""
return ConvertFrame(compiler_fn, hooks)
ConvertFrame的定义是
class ConvertFrame:
def __init__(
self,
compiler_fn: CompilerFn,
hooks: Hooks,
) -> None:
self._torchdynamo_orig_callable = compiler_fn
self._inner_convert = convert_frame_assert(compiler_fn, one_graph=False) // 转换函数
self._hooks = hooks
@property
def _clone_with_backend(self) -> Callable[[WrapBackendDebug], ConvertFrame]:
return lambda backend: convert_frame(backend, self._hooks)
def __call__(
self,
frame: DynamoFrameType,
cache_entry: Optional[CacheEntry],
hooks: Hooks,
frame_state: dict[str, Union[int, FrameStateSizeEntry]],
skip: int = 0,
) -> ConvertFrameReturn:
input_codes.add(frame.f_code)
counters["frames"]["total"] += 1
try:
result = self._inner_convert( // 具体执行转换
frame, cache_entry, hooks, frame_state, skip=skip + 1
)
counters["frames"]["ok"] += 1
return result
在初始化函数中,调用了convert_frame_assert函数,
def convert_frame_assert(
compiler_fn: CompilerFn,
one_graph: bool = True,
export: bool = False,
export_constraints: Optional[typing.Never] = None,
) -> ConvertFrameAssert:
"""Fully convert a frame into an FX graph"""
return ConvertFrameAssert(compiler_fn, one_graph, export, export_constraints)
在ConvertFrameAssert的__call__函数中(代码片段)
def __call__(
self,
frame: DynamoFrameType,
cache_entry: Optional[CacheEntry],
hooks: Hooks,
frame_state: dict[str, Union[int, FrameStateSizeEntry]],
*,
skip: int = 0,
) -> ConvertFrameReturn:
... 省略 ...
with compile_context(CompileContext(compile_id)):
return _compile(
frame.f_code,
frame.f_globals,
frame.f_locals,
frame.f_builtins,
frame.closure,
self._torchdynamo_orig_callable,
self._one_graph,
self._export,
self._export_constraints,
hooks,
cache_entry,
cache_size,
frame,
frame_state=frame_state,
compile_id=compile_id,
skip=skip + 1,
)
调用的是_compile函数,接下来的部分就与Ascend的aclgraph(三)TorchDynamo的第4节4 TorchDynamo模拟执行 & FX Graph构建一致了,下面不再展开。
打开调用栈堆栈,也可以清晰的看到。
/home/torchair/test_ge.py(37)<module>()
-> out = opt_model(x, y)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py(1532)_wrapped_call_impl()
-> return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py(1541)_call_impl()
-> return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/eval_frame.py(451)_fn()
-> return fn(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py(1532)_wrapped_call_impl()
-> return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py(1541)_call_impl()
-> return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(921)catch_errors()
-> return callback(frame, cache_entry, hooks, frame_state, skip=1) // 调用回调函数convert_frame
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(786)_convert_frame()
-> result = inner_convert(
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(400)_convert_frame_assert()
-> return _compile( // 调用compile
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/contextlib.py(79)inner()
-> return func(*args, **kwds)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(676)_compile()
-> guarded_code = compile_inner(code, one_graph, hooks, transform) 调用compile_inner
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/utils.py(262)time_wrapper()
-> r = func(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(535)compile_inner()
-> out_code = transform_code_object(code, transform) // 代码转换,负责字节码的编译
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/bytecode_transformation.py(1036)transform_code_object()
-> transformations(instructions, code_options)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(165)_fn()
-> return fn(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py(500)transform()
-> tracer.run()
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/symbolic_convert.py(2149)run()
-> super().run()
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/symbolic_convert.py(810)run()
-> and self.step()
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/symbolic_convert.py(773)step()
-> getattr(self, inst.opname)(inst)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/symbolic_convert.py(2268)RETURN_VALUE()
-> self.output.compile_subgraph(
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/output_graph.py(981)compile_subgraph()
-> self.compile_and_call_fx_graph(tx, list(reversed(stack_values)), root)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/contextlib.py(79)inner()
-> return func(*args, **kwds)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/output_graph.py(1178)compile_and_call_fx_graph()
-> compiled_fn = self.call_user_compiler(gm) // 开始调用用户自定义的compiler
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/utils.py(262)time_wrapper()
-> r = func(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/output_graph.py(1232)call_user_compiler()
-> compiled_fn = compiler_fn(gm, self.example_inputs())
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/repro/after_dynamo.py(117)debug_wrapper()
-> compiled_gm = compiler_fn(gm, example_inputs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/__init__.py(1770)__call__()
-> return self.compiler_fn(model_, inputs_, **self.kwargs)
> /usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(423)_npu_backend()
-> compiler = get_compiler(compiler_config) // 调用了到了自定义的backend函数_npu_backend
通过如上的代码注释,相信大家对整体流程就应该串起来了。从callback的设置,到callback的执行。_npu_backend中的最后一个执行函数是aot_module_simplified,接着往下
-> return aot_module_simplified(gm, example_inputs, fw_compiler=fw_compiler, bw_compiler=compiler,
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/aot_autograd.py(903)aot_module_simplified()
-> compiled_fn = create_aot_dispatcher_function(
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/utils.py(262)time_wrapper()
-> r = func(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/aot_autograd.py(628)create_aot_dispatcher_function()
-> compiled_fn = compiler_fn(flat_fn, fake_flat_args, aot_config, fw_metadata=fw_metadata)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/runtime_wrappers.py(443)aot_wrapper_dedupe()
-> return compiler_fn(flat_fn, leaf_flat_args, aot_config, fw_metadata=fw_metadata)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/runtime_wrappers.py(648)aot_wrapper_synthetic_base()
-> return compiler_fn(flat_fn, flat_args, aot_config, fw_metadata=fw_metadata)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/jit_compile_runtime_wrappers.py(119)aot_dispatch_base()
-> compiled_fw = compiler(fw_module, updated_flat_args)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(414)gear_compiler()
-> return compiler(gm, example_inputs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(389)wrapped_compiler()
-> return compiler(gm, example_inputs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/_utils/error_code.py(43)wapper()
-> return func(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(286)__call__()
-> return self._get_compiled_gm(gm, example_inputs) // 执行_NpuFxCompiler中的__call__函数
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(322)_get_compiled_gm()
-> return _GmRunner(self._gen_compiled_gm(gm, example_inputs)) // _GmRunner对象
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(348)_gen_compiled_gm()
-> concrete_graph: ConcreteGraphBase = _NpuGraphConverter(
> /usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(114)run()
-> optimized_fx = _optimize_fx(self.module) // _NpuGraphConverter的run函数
再看下GeConcreteGraph的__call__函数执行
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/eval_frame.py(451)_fn()
-> return fn(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/external_utils.py(36)inner()
-> return fn(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/aot_autograd.py(917)forward()
-> return compiled_fn(full_args)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py(89)g()
-> return f(*args)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/runtime_wrappers.py(100)runtime_wrapper()
-> all_outs = call_func_at_runtime_with_args(
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py(113)call_func_at_runtime_with_args()
-> out = normalize_as_list(f(args))
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/jit_compile_runtime_wrappers.py(152)rng_functionalization_wrapper()
-> return compiled_fw(args)
> /usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py(89)g()
-> return f(*args)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/npu_fx_compiler.py(261)__call__()
-> gm_result = self.runner(*args, **kwargs)
/usr/local/python3.10.17/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch_npu/dynamo/torchair/_ge_concrete_graph/fx2ge_converter.py(514)__call__()
-> enable_event_log = logger.getEffectiveLevel() <= EVENT_LEVEL
4 总结
对aclgraph相关的知识点,通过10篇的介绍,到这里就结束了。由于涉及到好几个代码库,这个系列的介绍都是偏向于逻辑上的串接,知道GeConcreteGraph和aclgraph的区别,以及从torch.compile触发,一步步是怎么将这些逻辑给串联起来的。
由于小编能力和时间有限,内容介绍不对的地方还请各位看官加以提出和修正,多多包涵。
期待Ascend上的图模式能力越来越好。

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容









所有评论(0)