用python进行计算机破案_用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析
用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析发布时间:2020-06-24 10:02:37来源:亿速云阅读:105作者:清晨这篇文章主要介绍用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析,文中示例代码介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们一定要看完!刑侦科推理题,不知是谁设计出来的,逻辑严整细致,有耐心看完题目的人就没几个。如果这真是刑警的日常考试题,我觉得他们实在是太厉害了,保证犯罪分子难逃法网。
用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析
发布时间:2020-06-24 10:02:37
来源:亿速云
阅读:105
作者:清晨
这篇文章主要介绍用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析,文中示例代码介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们一定要看完!
刑侦科推理题,不知是谁设计出来的,逻辑严整细致,有耐心看完题目的人就没几个。如果这真是刑警的日常考试题,我觉得他们实在是太厉害了,保证犯罪分子难逃法网。

编程遍历,这个逻辑本身很普通。但程序中有几个有趣的点值得一提。
首先是十道题,每题有4种可能的选项,全部为4^10=1M,约100万种可能,可以利用python的yield功能,避免将这么多中间结果保存起来。def makeList(choose, n):
if n==1:
for x in choose:
yield x
a= makeList(choose, n-1)
for item in a:
b= list(item)
for x in choose:
c= b.copy()
c.append(x)
yield c
另一个问题就是怎样把这些题目和选项完整地形式化。
就不一一讲解了,代码逻辑很清晰,直接上代码。注意:所有加fake的函数,代表对题目的略写,仅保证了选项正确,而没有保证非选项错误。
之所以这样处理,是希望假结果也出现。计算结果表明,第5、6、8使用略写法不会增加新的假结果,只有第4题放开才出现假结果。
为了和题目统一序号,避免出错,使用了1起,所以在列表前面增加了一个空选项。对其他题目不会有影响,但对第7题和第9题须注意一下,排除掉空选项的干扰。def q1(x):
return True
def q2(x):
i1= x[2]==A and x[5]==C
i2= x[2]==B and x[5]==D
i3= x[2]==C and x[5]==A
i4= x[2]==D and x[5]==B
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q3(x):
i1= x[3]==A and x[2]==x[4]==x[6] and x[2]!=A
i2= x[3]==B and x[2]==x[4]==x[3] and x[6]!=B
i3= x[3]==C and x[3]==x[4]==x[6] and x[2]!=C
i4= x[3]==D and x[2]==x[3]==x[6] and x[4]!=D
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q4(x):
i1= x[4]==A and x[1]==x[5] and x[2]!=x[7] and x[1]!=x[9] and x[6]!=x[10]
i2= x[4]==B and x[1]!=x[5] and x[2]==x[7] and x[1]!=x[9] and x[6]!=x[10]
i3= x[4]==C and x[1]!=x[5] and x[2]!=x[7] and x[1]==x[9] and x[6]!=x[10]
i4= x[4]==D and x[1]!=x[5] and x[2]!=x[7] and x[1]!=x[9] and x[6]==x[10]
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q4_fake(x):
i1= x[4]==A and x[1]==x[5]
i2= x[4]==B and x[2]==x[7]
i3= x[4]==C and x[1]==x[9]
i4= x[4]==D and x[6]==x[10]
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q5(x):
i1= x[5]==A and x[8]==x[5] and x[4]!=x[5] and x[9]!=x[5] and x[7]!=x[5]
i2= x[5]==B and x[8]!=x[5] and x[4]==x[5] and x[9]!=x[5] and x[7]!=x[5]
i3= x[5]==C and x[8]!=x[5] and x[4]!=x[5] and x[9]==x[5] and x[7]!=x[5]
i4= x[5]==D and x[8]!=x[5] and x[4]!=x[5] and x[9]!=x[5] and x[7]==x[5]
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q5_fake(x):
i1= x[5]==A and x[8]==x[5]
i2= x[5]==B and x[4]==x[5]
i3= x[5]==C and x[9]==x[5]
i4= x[5]==D and x[7]==x[5]
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q6(x):
i1= x[6]==A and (x[8]==x[2]==x[4]) and not(x[1]==x[6]==x[8]) and not(x[3]==x[10]==x[8]) and not(x[5]==x[9]==x[8])
i2= x[6]==B and not(x[8]==x[2]==x[4]) and (x[1]==x[6]==x[8]) and not(x[3]==x[10]==x[8]) and not(x[5]==x[9]==x[8])
i3= x[6]==C and not(x[8]==x[2]==x[4]) and not(x[1]==x[6]==x[8]) and (x[3]==x[10]==x[8]) and not(x[5]==x[9]==x[8])
i4= x[6]==D and not(x[8]==x[2]==x[4]) and not(x[1]==x[6]==x[8]) and not(x[3]==x[10]==x[8]) and (x[5]==x[9]==x[8])
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q6_fake(x):
i1= x[6]==A and (x[8]==x[2]==x[4])
i2= x[6]==B and (x[1]==x[6]==x[8])
i3= x[6]==C and (x[3]==x[10]==x[8])
i4= x[6]==D and (x[5]==x[9]==x[8])
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q7(x):
x0=x[1:]
mn= min(x0, key=x0.count)
i1= x[7]==A and mn==C
i2= x[7]==B and mn==B
i3= x[7]==C and mn==A
i4= x[7]==D and mn==D
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q8_fake(x):
i1= x[8]==A and abs(ord(x[7])- ord(x[1]))!=1
i2= x[8]==B and abs(ord(x[5])- ord(x[1]))!=1
i3= x[8]==C and abs(ord(x[2])- ord(x[1]))!=1
i4= x[8]==D and abs(ord(x[10])- ord(x[1]))!=1
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q9(x):
i1= x[9]==A and xor(x[1]==x[6], x[6]==x[5])
i2= x[9]==B and xor(x[1]==x[6], x[10]==x[5])
i3= x[9]==C and xor(x[1]==x[6], x[2]==x[5])
i4= x[9]==D and xor(x[1]==x[6], x[9]==x[5])
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
def q10(x):
x0=x[1:]
m1= max(x0, key=x0.count)
m2= min(x0, key=x0.count)
mx= x0.count(m1)
mn= x0.count(m2)
i1= x[10]==A and mx- mn==3
i2= x[10]==B and mx- mn==2
i3= x[10]==C and mx- mn==4
i4= x[10]==D and mx- mn==1
return i1 or i2 or i3 or i4
注意看一下第9题,其中的xor不是python自带的函数,它的定义很简单。def xor(a, b):
return (a or b) and not(a and b)
最后遍历得到结果:def testAnswer(x):
a= q1(x)
a= a and q2(x)
a= a and q3(x)
a= a and q4_fake(x)
a= a and q5_fake(x)
a= a and q6_fake(x)
a= a and q7(x)
a= a and q8_fake(x)
a= a and q9(x)
a= a and q10(x)
return a
A='A'
B='B'
C='C'
D='D'
a= makeList([A, B, C, D], 10)
c= 0
for x in a:
x.insert(0, '')
c+=1
if testAnswer(x):
print(c, x)
print('tested %d times' % c)
运行结果
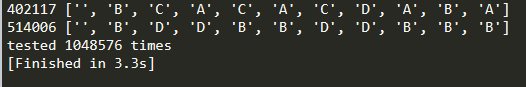
稍做验证即可知道,第一个答案是正确的,第二个即前文所提的假结果。
以上是用Python对刑侦科推理题进行分析的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!希望分享的内容对大家有帮助,更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)