TensorRT部署YoloX:int8量化
使用基于tensorrt完成YoloX的int8量化工作,减小模型的内存占用和提高推理速度
1、INT8量化原理
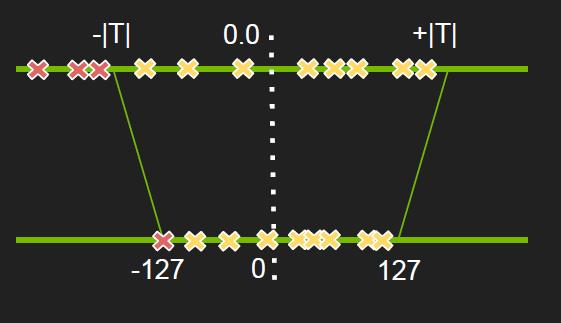
TensorRT 中 int8 量化的基本原理是为了减少模型推理时的内存占用和提高计算性能,将原来的 float32 数据类型转换为 int8。int8量化可以减小神经网络模型大小,同时将网络中大量的float32的乘法计算转换为int8数据间的乘法计算,对算法进行加速。这个过程需要针对每一层的输入 tensor 和网络学习到的参数进行。但是不同网络结构的不同 layer 的激活值分布很不一样,因此合理的量化方式应该适用于不同的激活值分布,并且减小信息损失。
在 TensorRT 中,int8 量化过程需要编写校准器类进行校准。校准的目的是寻找一个最佳的量化参数,以使得 int8 表示的数据与原始的 float32 数据之间的误差最小。在这个过程中,可以使用相对熵(也叫 kl 散度)来衡量不同的 int8 分布与原来的 float32 分布之间的差异程度。
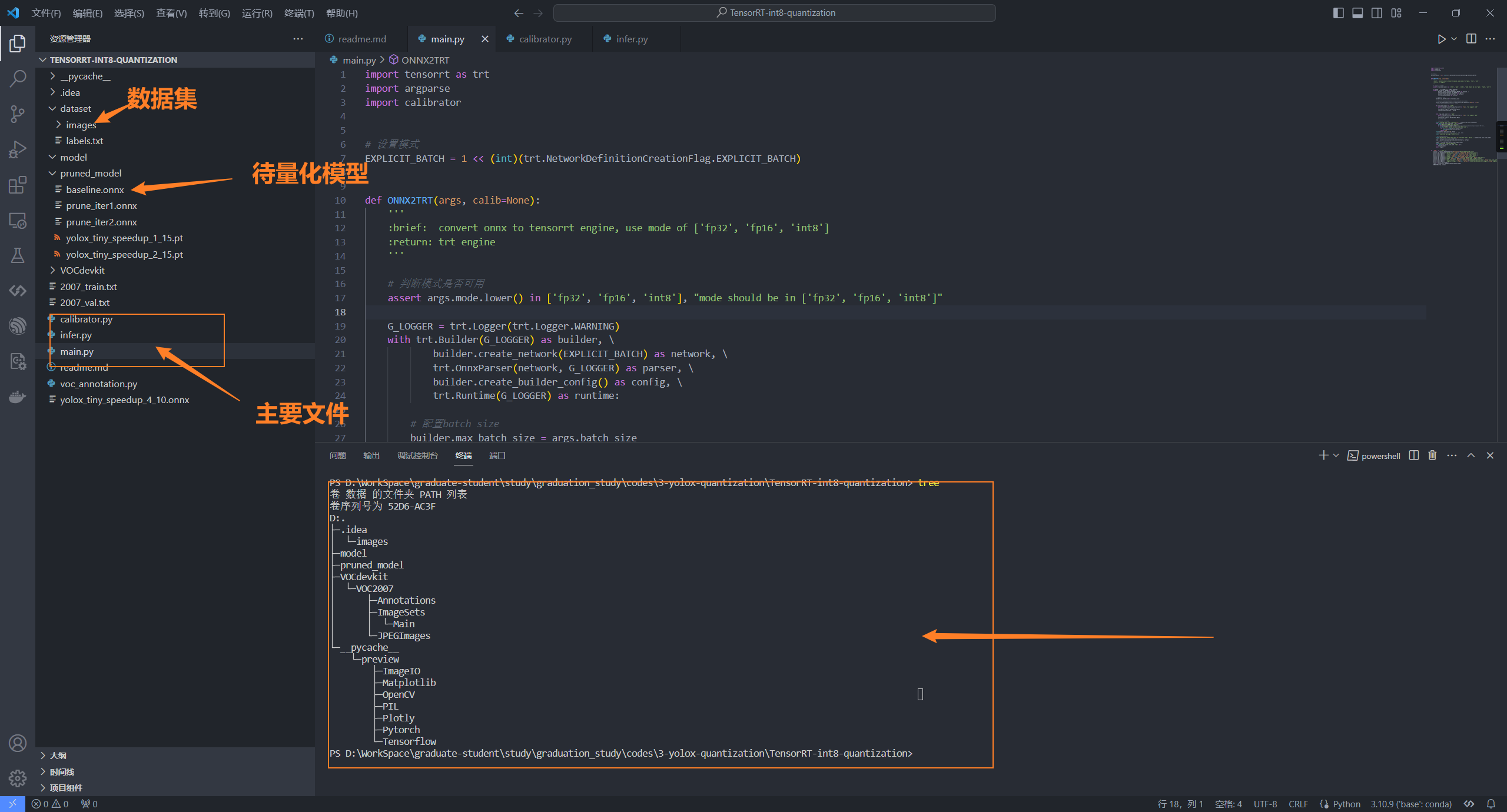
2、工程目录结构
3、校准数据类(calibrator.py)
用于产生在量化过程中所需的校准数据,不同的模型可参考这份代码进行修改,完成自己模型的部署
import cv2
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
def preprocess_input(image):
"""
图像预处理
"""
image = image/255.0
image = image-np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
image = image/np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# image -= np.array([0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
# image /= np.array([0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
return image
class YOLOXEntropyCalibrator(trt.IInt8EntropyCalibrator2):
def __init__(self, args, files_path='2007_train.txt'):
trt.IInt8EntropyCalibrator2.__init__(self)
self.cache_file = 'YOLOX.cache'
self.batch_size = args.batch_size
self.Channel = args.channel
self.Height = args.height
self.Width = args.width
# self.transform = transforms.Compose([
# transforms.Resize([self.Height, self.Width]), # [h,w]
# transforms.ToTensor(),
# ])
# 获取数据集中图像的路径列表
self._txt_file = open(files_path, 'r')
self._lines = self._txt_file.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(self._lines) #./dataset/images/image_0.jpg;278.35,98.2776,769.969,530.35,1
self.imgs = [line.strip().split(" ")[0] for line in self._lines]#所有文件路径
# 初始化内存
self.batch_idx = 0
self.max_batch_idx = len(self.imgs) // self.batch_size
self.data_size = trt.volume([self.batch_size, self.Channel, self.Height, self.Width]) * trt.float32.itemsize
self.device_input = cuda.mem_alloc(self.data_size)
def next_batch(self):
"""
读取一个batch的图像数据
"""
if self.batch_idx < self.max_batch_idx:
#***********读取一个batch的文件**************#
batch_files = self.imgs[self.batch_idx * self.batch_size: \
(self.batch_idx + 1) * self.batch_size]
batch_imgs = np.zeros((self.batch_size, self.Channel, self.Height, self.Width),
dtype=np.float32)
for i, f in enumerate(batch_files):
# img = Image.open(f)
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(f, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
scale_h = 480 / img.shape[0]
scale_w = 640 / img.shape[1]
scale = min([scale_w, scale_h])
img = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=scale, fy=scale)
empty_img = np.ones((480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
empty_img[0:img.shape[0], 0:img.shape[1], :] = img
empty_img = empty_img.astype(np.float32)
img = preprocess_input(empty_img)
img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = img.astype(np.float32)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# 判断字节是否与缓冲区对齐
assert (img.nbytes == self.data_size / self.batch_size), 'not valid img!' + f
batch_imgs[i] = img
self.batch_idx += 1
print("batch:[{}/{}]".format(self.batch_idx, self.max_batch_idx))
return np.ascontiguousarray(batch_imgs)
else:
return np.array([])
def get_batch_size(self):
"""
获取batch大小
"""
return self.batch_size
def get_batch(self, names, p_str=None):
"""
获取一个batch的图像数据,并拷贝到device内存中
"""
try:
batch_imgs = self.next_batch()
if batch_imgs.size == 0 or batch_imgs.size != self.batch_size * self.Channel * self.Height * self.Width:
return None
cuda.memcpy_htod(self.device_input, batch_imgs.astype(np.float32))
return [int(self.device_input)]
except Exception as e:
print("发生异常,异常为:{}".format(e))
return None
def read_calibration_cache(self):
"""
读取缓存数据
"""
# 如果存在校准集的缓存,则使用现有缓存,否则返回空值
if os.path.exists(self.cache_file):
print("succeed finding cache file:{}".format(self.cache_file))
with open(self.cache_file, "rb") as f:
return f.read()
else:
print("failed finding int8 cache!")
return
def write_calibration_cache(self, cache):
"""
写入缓存数据
"""
with open(self.cache_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(cache)
print("succeed saving int8 cache!")4、模型转换代码(main.py)
在所有算子都支持的情况下,可将onnx转换为fp32、fp16、int8的推理引擎文件,所有模型转换可参考这份代码
import tensorrt as trt
import argparse
import calibrator
# 设置模式
EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)
def ONNX2TRT(args, calib=None):
'''
:brief: convert onnx to tensorrt engine, use mode of ['fp32', 'fp16', 'int8']
:return: trt engine
'''
# 判断模式是否可用
assert args.mode.lower() in ['fp32', 'fp16', 'int8'], "mode should be in ['fp32', 'fp16', 'int8']"
G_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
with trt.Builder(G_LOGGER) as builder, \
builder.create_network(EXPLICIT_BATCH) as network, \
trt.OnnxParser(network, G_LOGGER) as parser, \
builder.create_builder_config() as config, \
trt.Runtime(G_LOGGER) as runtime:
# 配置batch size
builder.max_batch_size = args.batch_size
#配置tensorrt的推理缓冲区大小,即构建阶段可用的显存大小
config.set_memory_pool_limit(trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE,4096*(1 << 30))
# config.max_workspace_size = 1 << 50
if args.mode.lower() == 'int8':
assert (builder.platform_has_fast_int8 == True), "not support int8"
# 配置int8量化所需的参数及校准集
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.INT8)
config.int8_calibrator = calib
elif args.mode.lower() == 'fp16':
assert (builder.platform_has_fast_fp16 == True), "not support fp16"
# 配置fp16模式下的参数
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.FP16)
# config.fp16
# 加载onnx模型,并解析
print('Loading ONNX file from path {}...'.format(args.onnx_file_path))
with open(args.onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
print('Beginning ONNX file parsing')
if not parser.parse(model.read()):#parser是tensorrt的onnx解析类,声明位置见20行
print("ERROR: Failed to parse the ONNX file.")
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
return None
print(network.get_input(0).shape)
# network.get_input(0).shape = [1, 3, 640, 960]
print('Completed parsing of ONNX file')
# 构建序列化引擎文件
print('Building an engine from file {}; this may take a while...'.format(args.onnx_file_path))
# 根据配置及解析的网络构建序列化会话
plan = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
# 反序列化加载构建推理引擎
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(plan)
print("Completed creating Engine")
with open(args.engine_file_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(plan)
return engine
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Pytorch2TensorRT args")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=8, help='batch_size')
parser.add_argument("--channel", type=int, default=3, help='input channel')
parser.add_argument("--height", type=int, default=480, help='input height')
parser.add_argument("--width", type=int, default=640, help='input width')
parser.add_argument("--cache_file", type=str, default='YOLOX.cache', help='cache_file')
parser.add_argument("--mode", type=str, default='int8', help='fp32, fp16 or int8')
parser.add_argument("--onnx_file_path", type=str, default='pruned_model/baseline.onnx', help='onnx_file_path')
parser.add_argument("--engine_file_path", type=str, default='./model/optim_model_int8.engine', help='engine_file_path')
args = parser.parse_args()
calib = calibrator.YOLOXEntropyCalibrator(args)
ONNX2TRT(args, calib)
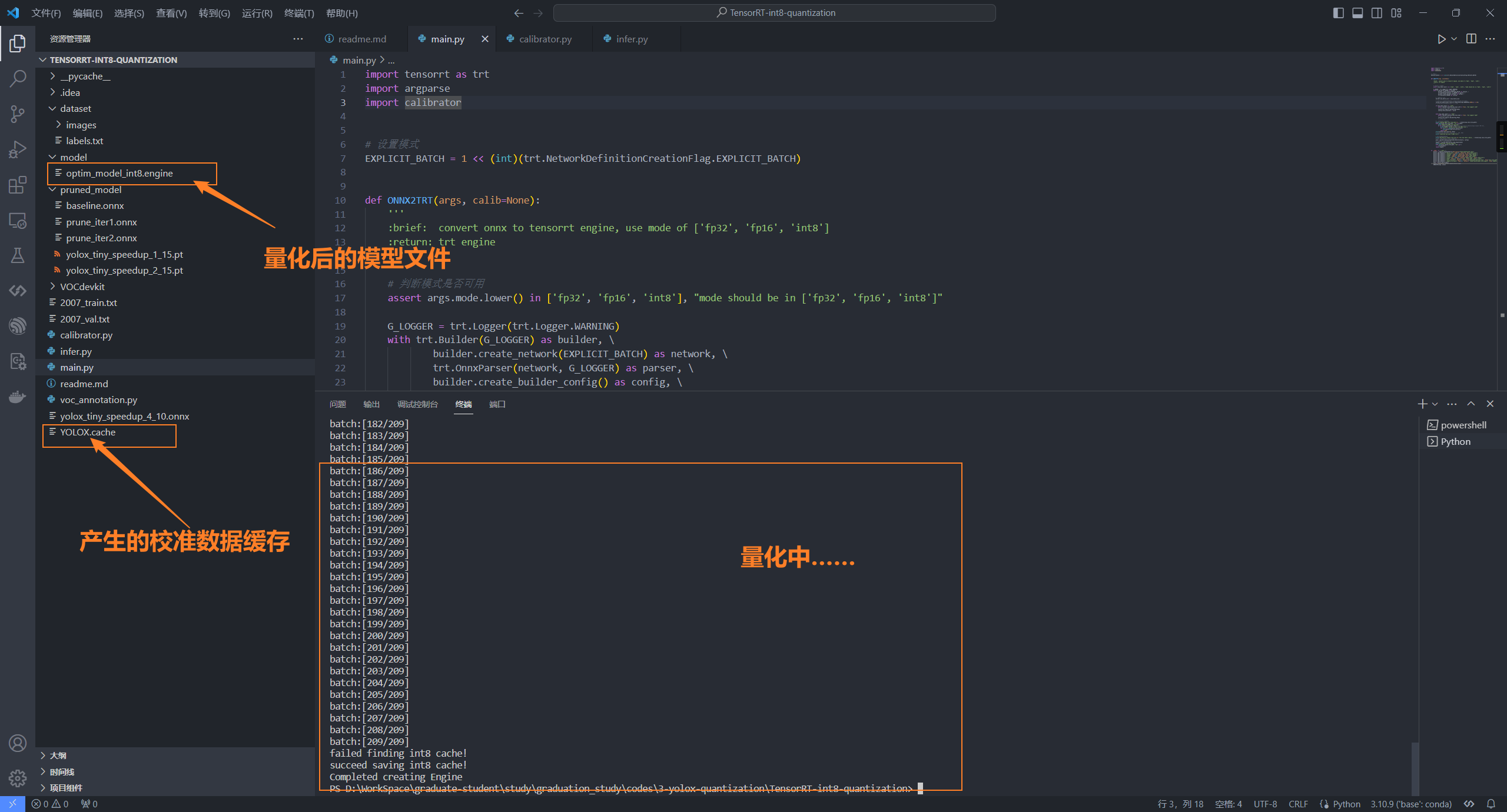
运行main.py
5、模型测试(infer.py)
推理代码如下
import os
import time
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
import tensorrt as trt
import numpy as np
import cv2
class YOLOXInfer(object):
def __init__(self, engine_file_path,image_size):
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
# 建立模型,创建上下文管理器
self.engine = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER).deserialize_cuda_engine(open(engine_file_path, 'rb').read())
self.context = self.engine.create_execution_context()
self.context.active_optimization_profile = 0
self.strides = [8,16,32]
self.height = image_size[0] # 480
self.width = image_size[1]
outshape_l = self.context.get_binding_shape(1)
outshape_m = self.context.get_binding_shape(2)
outshape_s = self.context.get_binding_shape(3)
self.context.get_binding_shape(1)
self.output_l = np.empty(outshape_l, dtype=np.float32)
self.output_m = np.empty(outshape_m, dtype=np.float32)
self.output_s = np.empty(outshape_s, dtype=np.float32)
self.d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(1*4*image_size[0]*image_size[1]*3)
self.d_output_l = cuda.mem_alloc(1*self.output_l.dtype.itemsize*self.output_l.size)
self.d_output_m = cuda.mem_alloc(1*self.output_m.dtype.itemsize*self.output_m.size)
self.d_output_s = cuda.mem_alloc(1*self.output_s.dtype.itemsize*self.output_s.size)
self.bindings = [int(self.d_input), int(self.d_output_l), int(self.d_output_m), int(self.d_output_s)]
self.stream = cuda.Stream()
def preprocess_input(self,img):
scale_h = self.height / img.shape[0]
scale_w = self.width / img.shape[1]
scale = min([scale_w, scale_h])
img = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=scale, fy=scale)
empty_img = np.ones((self.height, self.width, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
empty_img[0:img.shape[0], 0:img.shape[1], :] = img
image = empty_img.astype(np.float32)
image /= 255.0
image -= np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
image /= np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
image = np.transpose(image, (2, 0, 1))
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
return image,scale
def infer(self, img):
img,scale = self.preprocess_input(img)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img,dtype=np.float32)
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(self.d_input, img, self.stream)
self.context.execute_async(bindings=self.bindings, stream_handle=self.stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(self.output_s, self.d_output_s, self.stream)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(self.output_m, self.d_output_m, self.stream)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(self.output_l, self.d_output_l, self.stream)
self.stream.synchronize()
self.output = [self.output_l, self.output_m, self.output_s]
return self.parse_output(self.output,scale)
def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
def desigmoid(self,y):
return -np.log(1 / y - 1)
def parse_output(self, output,scale):
rects = []
labels = []
confs = []
for k,result in enumerate(output):
stride = self.strides[k]
for i in range(result.shape[2]):
for j in range(result.shape[3]):
isObj = self.sigmoid(result[0, 4, i, j])
if isObj > 0.5:
conf = isObj * self.sigmoid(np.max(result[0, 5:, i, j]))
if conf > 0.5:
label = np.argmax(result[0, 5:, i, j])
x = result[0, 0, i, j]
x += j
x *= stride
y = result[0, 1, i, j]
y += i
y *= stride
w = result[0, 2, i, j]
w = np.exp(w)
w *= stride
h = result[0, 3, i, j]
h = np.exp(h)
h *= stride
x1 = int(max(x - w / 2, 0))
y1 = int(max(y - h / 2, 0))
x2 = int(max(x + w / 2, 0))
y2 = int(max(y + h / 2, 0))
rects.append([x1, y1, x2, y2])
labels.append(label)
confs.append(conf)
boxes_ids = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(rects, confs, 0.2, 0.1)
objects = []
for boxes_id in boxes_ids:
x1 = rects[boxes_id][0]/scale
y1 = rects[boxes_id][1]/scale
x2 = rects[boxes_id][2]/scale
y2 = rects[boxes_id][3]/scale
label = labels[boxes_id]
conf = confs[boxes_id]
obj = {"label":label,"rect":[x1, y1, x2, y2],"conf":conf}
objects.append(obj)
return objects
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLOXInfer('./model/optim_model_fp32.engine',[480,640])
image_path = "./dataset/images"
image_list = os.listdir(image_path)
for file in image_list:
filename = os.path.join(image_path,file)
img = cv2.imread(filename,cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
start_time = time.time()
result = model.infer(img)
infer_time = time.time()-start_time
print("time:",infer_time)
for obj in result:
x1,y1,x2,y2 = obj["rect"]
print(obj["rect"])
ptLeftTop = (int(x1), int(y1))
ptRightBottom = (int(x2), int(y2))
point_color = (0, 255, 0) # BGR
thickness = 1
lineType = 4
cv2.rectangle(img, ptLeftTop, ptRightBottom, point_color, thickness, lineType)
cv2.putText(img,"FPS:{0:.3f}".format(1/infer_time),org=(0,40),fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,fontScale=1,color=(0,255,0),lineType=2)
cv2.putText(img,"{}".format(obj["label"]),org=(int(x1),int(y1)),fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,fontScale=1,color=(0,255,0),lineType=2)
cv2.imshow('result',img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
测试效果
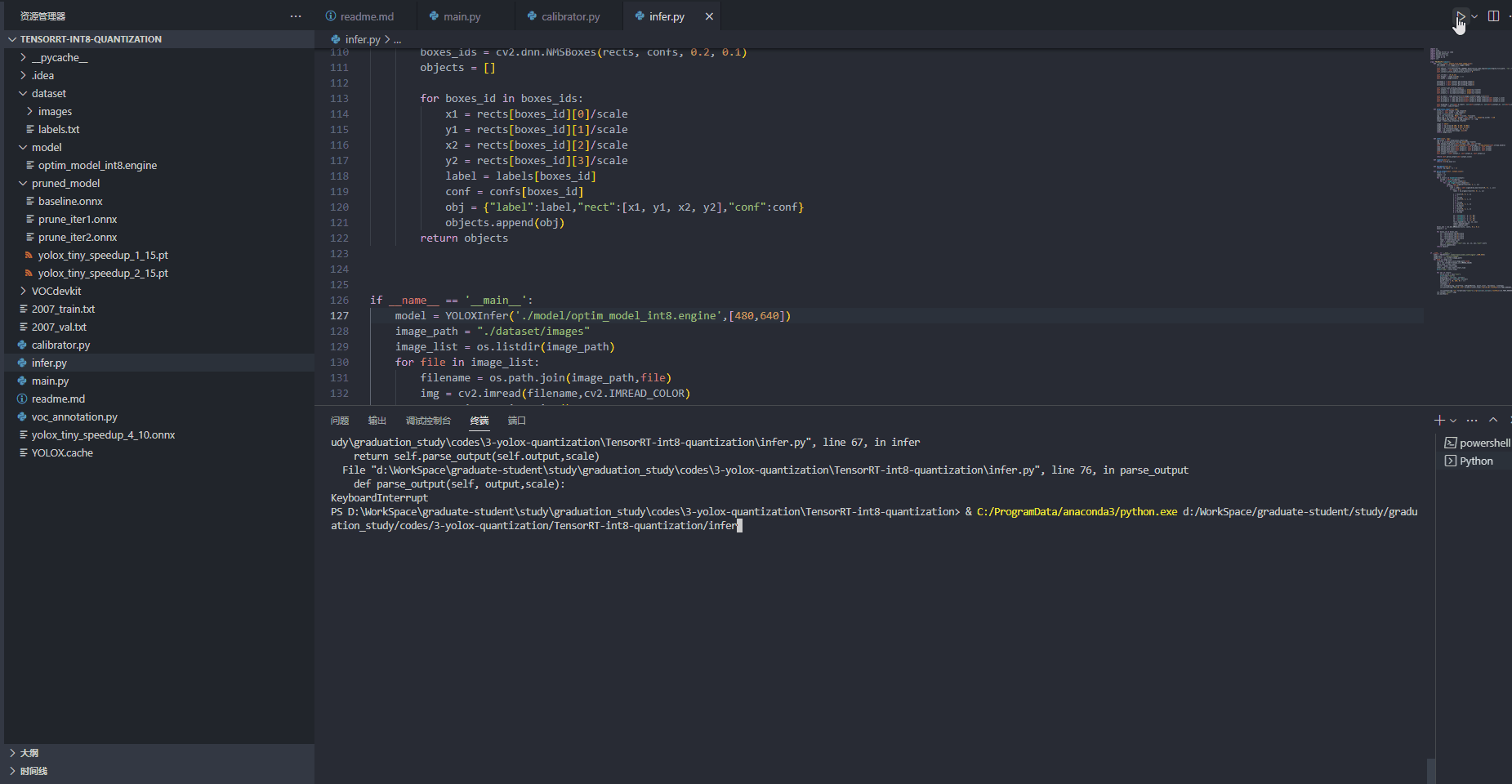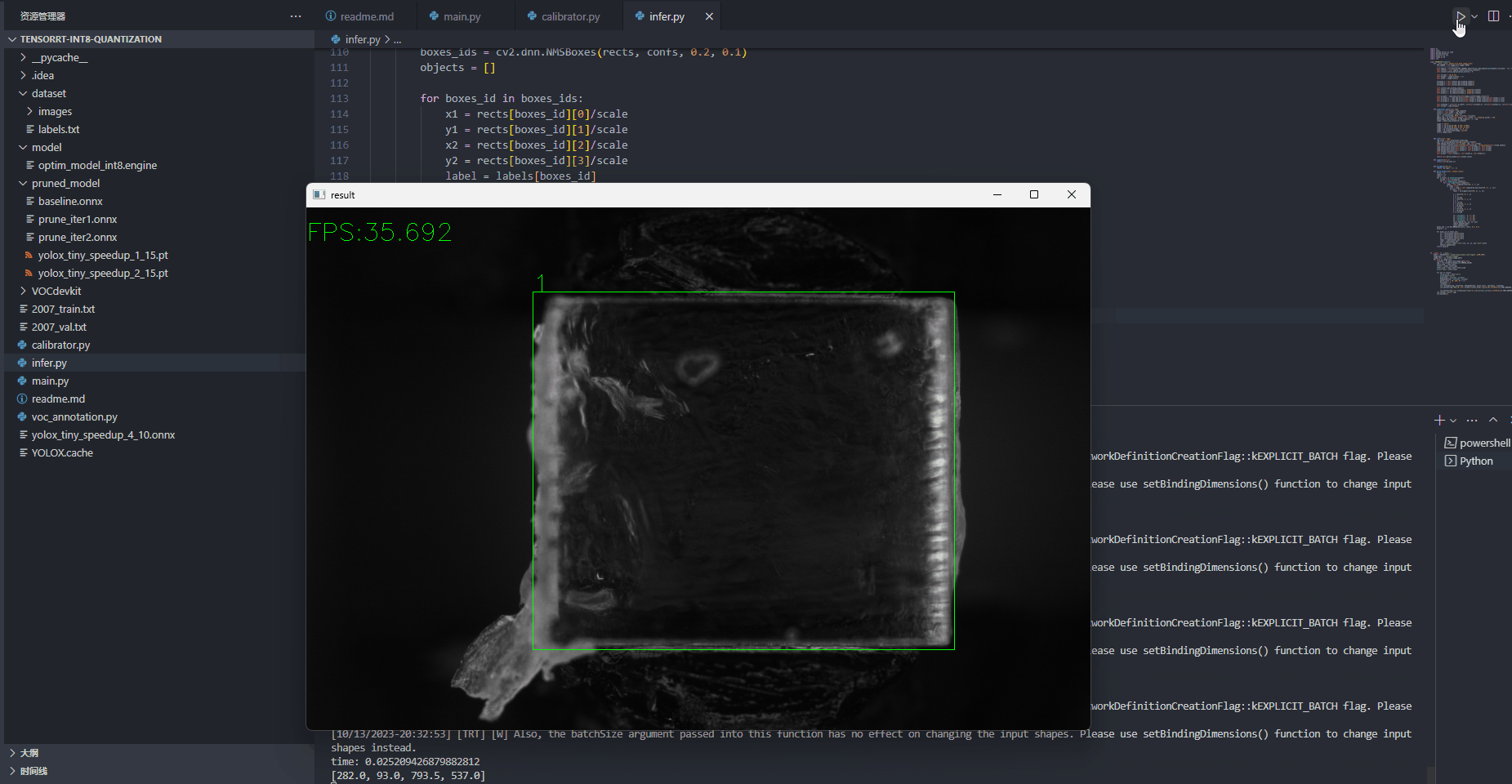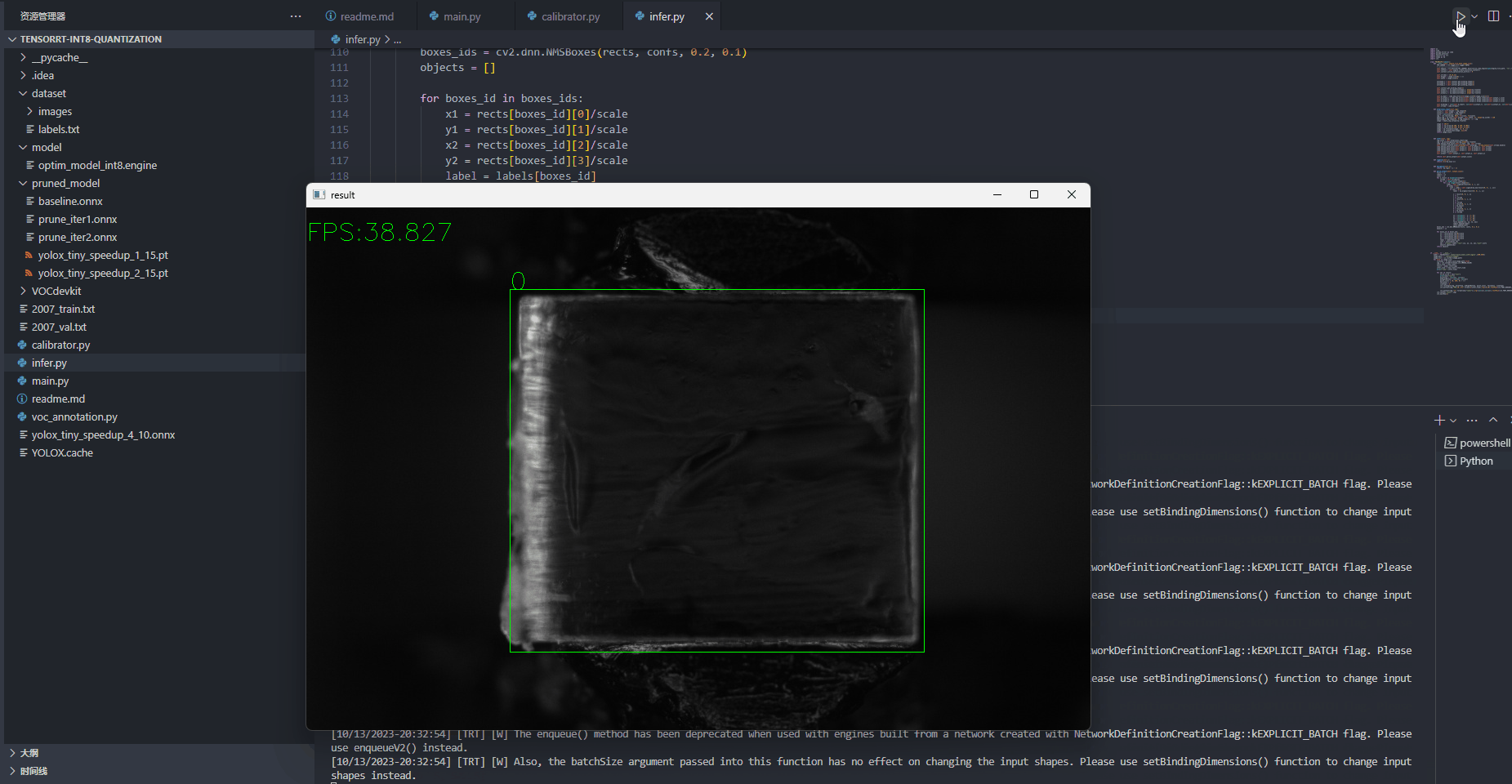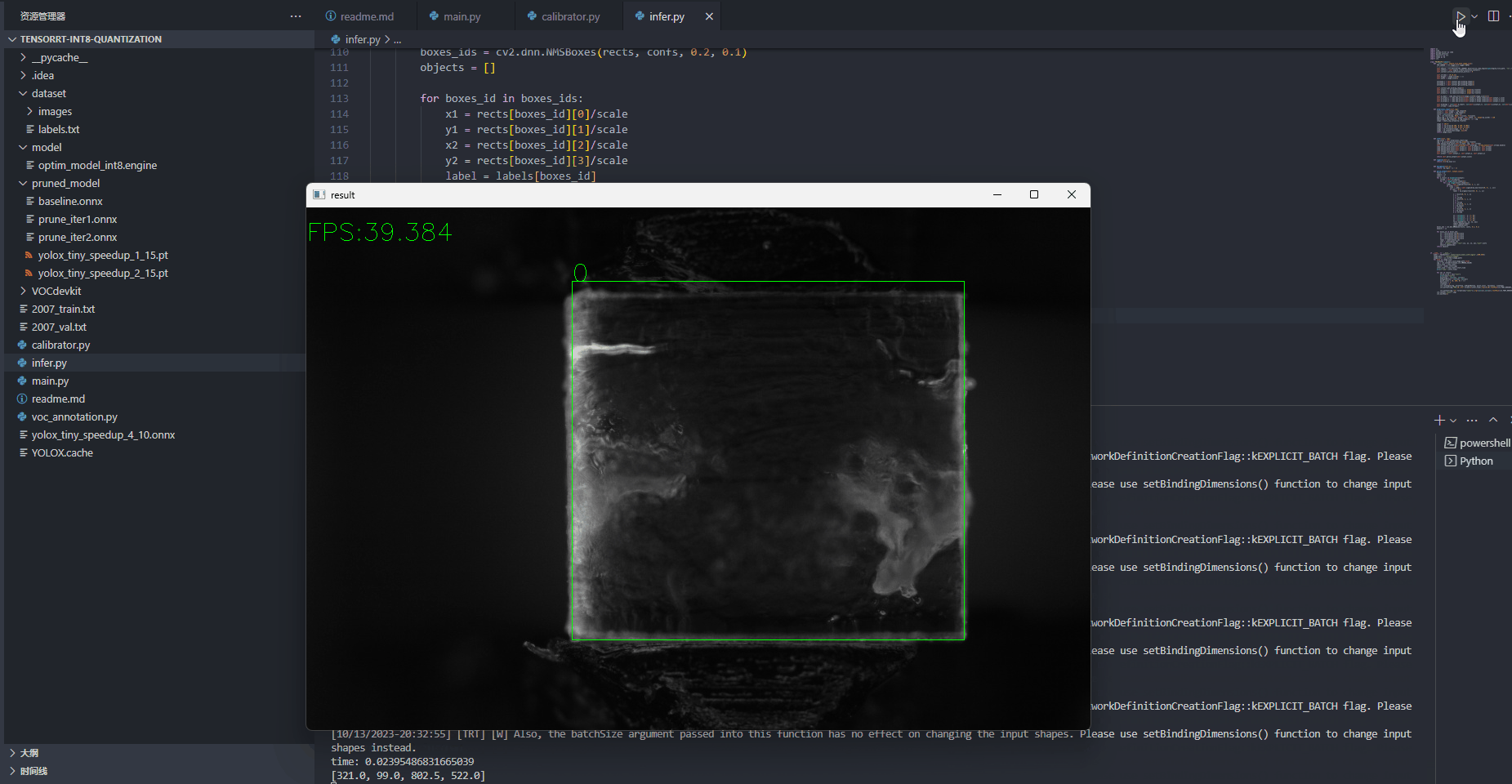
后续作者还会出plugin实现的相关分享,敬请期待!!!!

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)