[ICLR 2024]CLIP-MUSED: CLIP-Guided Multi-Subject Visual Neural Information Semantic Decoding
计算机-人工智能-脑信号解码图像分类

论文网址:[2402.08994] CLIP-MUSED: CLIP-Guided Multi-Subject Visual Neural Information Semantic Decoding
论文代码:https://github.com/CLIP-MUSED/CLIP-MUSED
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3.2. CLIP-based feature extraction of visual stimuli
2.3.3. Transformer-bsed fMRI feature extraction
2.4.5. Comparative experimental results
2.5. Discussion and Conclusion
1. 心得
(1)哥们儿做的实验有点少啊
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Challenge: neural information encoding, generalizing single subject to multiple subjects
②They proposed CLIP-guided Multi-sUbject visual neural information SEmantic Decoding (CLIP-MUSED) method
2.2. Introduction
①Existing fMRI decoding methods:
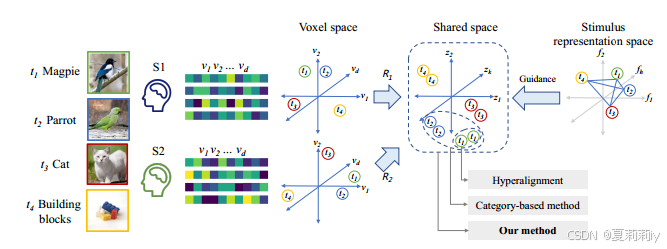
for 2 subjects with the same stimuli, existing works mapping the fMRI signals to voxel space. Then aggregate/cluster the fMRI signals with the same stimuli. However, it is hard to generalize. So another method clusters each categories.
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Overview
①Overall framework:
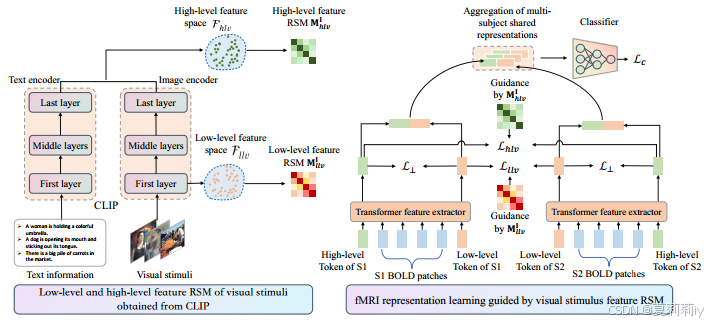
②: voxel space
③: the neural responses of the
-th subject in total
, where
is the number of image stimuli and
is the number of voxels(那为什么不是
)
④: pixel space of image stimuli
⑤: label space of image stimuli
⑥Classifier:
2.3.2. CLIP-based feature extraction of visual stimuli
①They extract low-level feature and high level feature by the first layer of image encoder and the average value of the last layer of the whole CLIP (image and text encoder)
②Representation similarity matrices (RSMs) and
is to quantify the similarity between
(batch size) visual stimuli in low-level and high-level feature spaces.
and
in
and
denote image similarity in
and
2.3.3. Transformer-bsed fMRI feature extraction
①Transformer process:
②Transformer-based fMRI feature extractor:
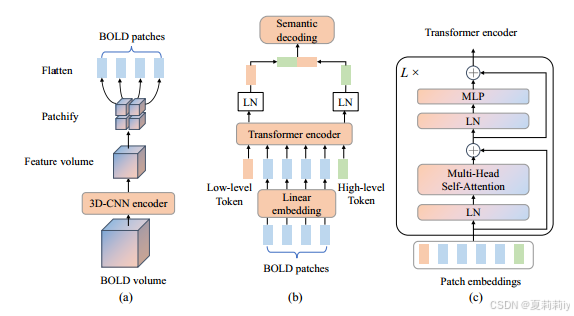
(a) they firstly reduce the dimension of BOLD volume and then patchify and flatten them, functions of (b) and (c) are:
2.3.4. Multi-subject shared neural response representation
①Similarity loss:
2.3.5. Semantic classifier
①Final representation:
②Semantic classification CE loss:
2.3.6. Optimization objective
①Orthogonal constraint to encourage the difference between low-level and high-level token representations:
②Final loss:
2.4. Experiments
2.4.1. Datasets
(1)HCP
①Subjects: 9 of 158
②Visual stimuli: four dynamic movie clips, each annotated with an 859-dimensional WordNet label
③Categories: labels which frequency higher than 0.1
(2)NSD
①Subjects: 8
②Visual stimuli: MSCOCO, each image has multiple labels from 80 categories. Different 9k stimulus for each subject and the same 1k for all the subjects
2.4.2. Baseline methods
①Types of compared methods: Single-subject decoding methods, multi-subject data aggregation methods, MS-EMB, Shared response model (SRM)
2.4.3. Parameter settings
(1)HCP
①3D-CNN: 6 layers, obtaining 7×8×7×512, and reshape to 392×512 (359 patches)
②Transformer blocks: 2
②Optimizer: Adam with 0.001 learning rate
③Batch size: 64
④Hyperparameter of loss weights:
(2)NSD
①Embedding layers: 512, 24
②Head: 8
③Batch size: 64
④Optimizer: Adam with 0.0001 learning rate
⑤Hyperparameter of loss weights:
2.4.4. Evaluation metrics
①Mean Average Precision (mAP), the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and Hamming distance
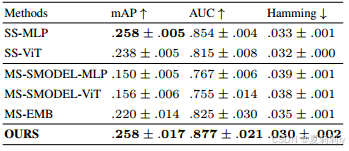
2.4.5. Comparative experimental results
①Performance on HCP:
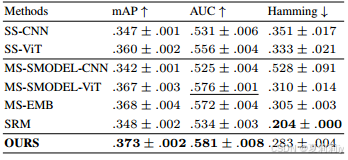
②Performance on NSD:
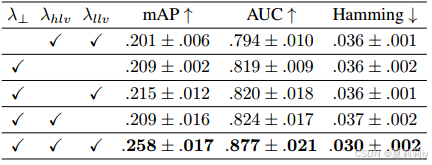
2.4.6. Ablation study
①Loss ablation:
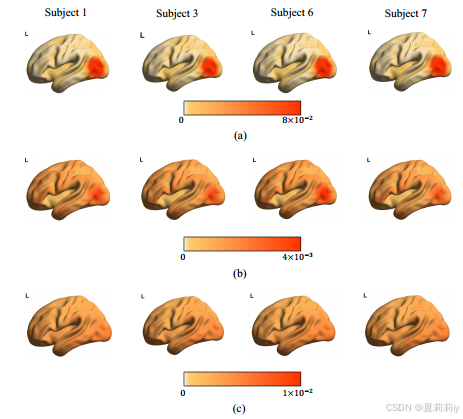
2.4.7. Visualization
①(a) low-level tokens, (b) high-level tokens, (c) attention map of MS-EMB method:
2.5. Discussion and Conclusion
~

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献27条内容
已为社区贡献27条内容









所有评论(0)