19.初识Pytorch之完整的模型套路-整理后的代码 Complete model routine - compiled code
**1**.Ready modelLeNet_5.pyfrom torch import nnclass LeNet_5(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LeNet_5, self).__init__()self.model = nn.Sequential(# input:3@32x32# 6@28x28nn.Conv2d(in
上一章 初识Pytorch之完整的模型套路-合在一个.py文件中 Complete model routine - in one .py file
本章是将上一章合在一起的代码,整理成更加符合可读性或者可用性的方式。
This chapter is a combination of code from the previous chapter, organized into a more readable or usable way.
此代码我已上传至我的GitHub,欢迎大家访问!
I have uploaded this code to my GitHub, and welcome to visit!
注意:本次实验的训练均在谷歌免费的GPU中进行,且谷歌免费的GPU每周可以使用30个小时,别问我为什么不用自己的服务器来跑,问就是穷。
PS:The training of this experiment is carried out in Google's free GPU, and Google's free GPU can be used for 30 hours a week. Don't ask me why I don't use my own server to run, it's just poor.
下一章,将如何使用GPU(cuda)对模型进行训练与测试(或者使用GPU训练,cpu测试)。
In the next chapter, I will tell you how to use GPU (cuda) to train and test the model (or use GPU training, and cpu testing).
如果感兴趣谷歌免费的GPU如何使用,点赞或者收藏超过十个,我就出一期如何使用谷歌免费的GPU。
**1**.Ready model
对之前的LeNet_5模型进行了优化,加入了激活函数
The previous LeNet_5 model was optimized and activation functions were added.
LeNet_5.py
from torch import nn
class LeNet_5(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet_5, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
# input:3@32x32
# 6@28x28
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5, padding=0, stride=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 6@14x14
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0),
# 16@10x10
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, padding=0, stride=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 16@5x5
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Linear(84, 10),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
**2**.Ready train
在谷歌免费的GPU中,使用cuda进行训练
In Google's free GPU,use cuda for training.
train_GPU.py
PS:参数是我凭着感觉和设置的,没有调参,大家可以自己去调试
The parameters are set by my feeling, there is no parameter adjustment, you can debug it yourself.
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from LeNet_5 import *
import torchvision
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# 1. torch choose cuda or cpu
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
# 2.Create SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter("log_loss")
# 3.Ready dataset
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="data", train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 4.Length
train_dataset_size = len(train_dataset)
print("the train dataset size is {}".format(train_dataset_size))
# 5.DataLoader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=64)
# 6.Create model
model = LeNet_5()
# a.add cuda
model = model.to(device=device)
# 7.Create loss
cross_entropy_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# b.add cuda
cross_entropy_loss = cross_entropy_loss.to(device=device)
# 8.Optimizer
learning_rate = 1e-2
optim = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 9. Set some parameters to control loop
# epoch
epoch = 80
total_train_step = 0
for i in range(epoch):
print(" -----------------the {} number of training epoch --------------".format(i + 1))
model.train()
for data in train_dataloader:
# c.add cuda
imgs, targets = data
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
outputs = model(imgs)
loss_train = cross_entropy_loss(outputs, targets)
optim.zero_grad()
loss_train.backward()
optim.step()
total_train_step = total_train_step + 1
if total_train_step % 100 == 0:
print("the training step is {} and its loss of model is {}".format(total_train_step, loss_train.item()))
writer.add_scalar("train_loss", loss_train.item(), total_train_step)
if total_train_step % 10000 == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "model_save/model_{}_GPU.pth".format(total_train_step))
print("the model of {} training step was saved! ".format(total_train_step))
if i == (epoch - 1):
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "model_save/model_{}_GPU.pth".format(total_train_step))
print("the model of {} training step was saved! ".format(total_train_step))
writer.close()
result:
!python train_GPU.py train
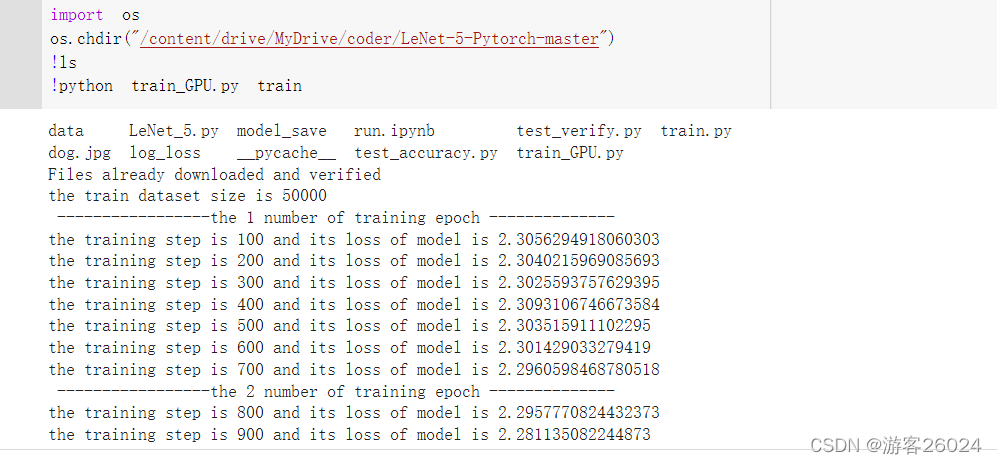
Tensorboard:train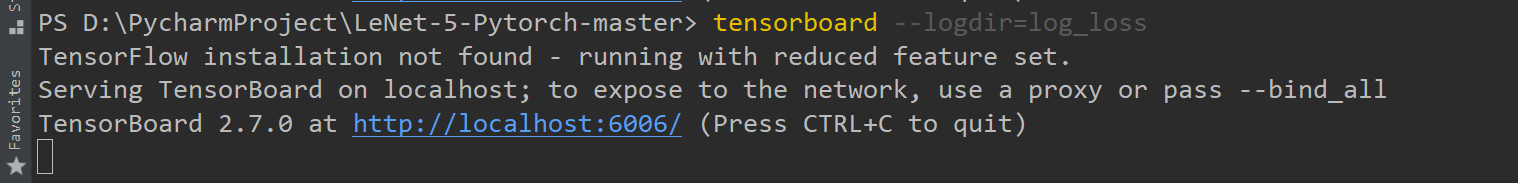
**3**.test_accuracy
使用cuda进行训练,之后用cpu进行测试
Use cuda for training, then test with cpu.
test_accuracy_GPU.py

import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from LeNet_5 import *
import torchvision
# test
# 1.Create model
model = LeNet_5()
# 2.Ready Dataset
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="data", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 3.Length
test_dataset_size = len(test_dataset)
print("the test dataset size is {}".format(test_dataset_size))
# 4.DataLoader
test_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=64)
# 5. Set some parameters for testing the network
total_accuracy = 0
# test
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
model_load = torch.load("model_save/model_62500_GPU.pth", map_location=torch.device("cpu"))
model.load_state_dict(model_load)
outputs = model(imgs)
accuracy = (outputs.argmax(1) == targets).sum()
total_accuracy = total_accuracy + accuracy
accuracy = total_accuracy / test_dataset_size
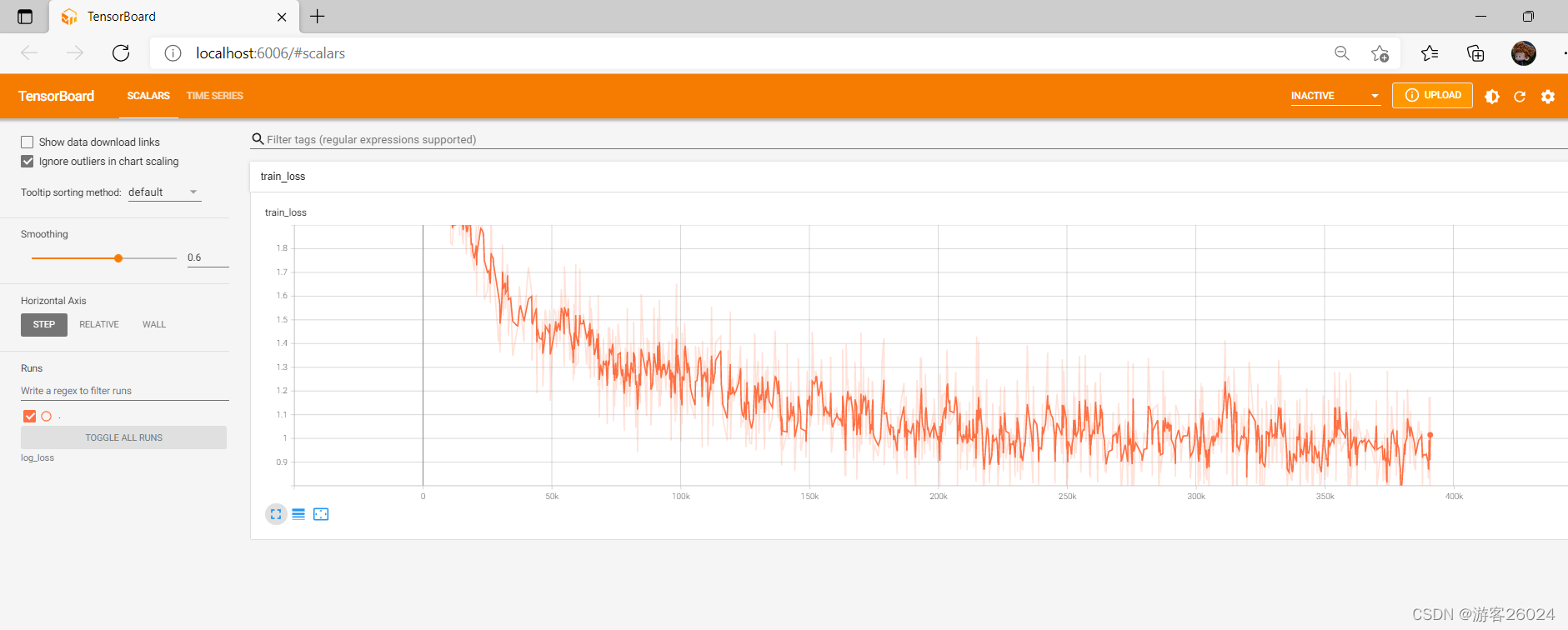
print("the total accuracy is {}".format(accuracy))
result:
(run) python test_accuracy_GPU.py
**4**.test_verify
使用cuda进行训练,之后用cpu进行验证
Use cuda for training, then verify with cpu.
test_verify_GPU.py

import torch
import cv2
import torchvision
from LeNet_5 import *
# test
# 1.Create model
model = LeNet_5()
# 2.Ready Data
img = cv2.imread("dog.jpg")
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Resize((32, 32))])
img = transform(img)
img = img.reshape(1, 3, 32, 32)
# test
model.eval()
model_load = torch.load("model_save/model_62500_GPU.pth", map_location=torch.device("cpu"))
model.load_state_dict(model_load)
with torch.no_grad():
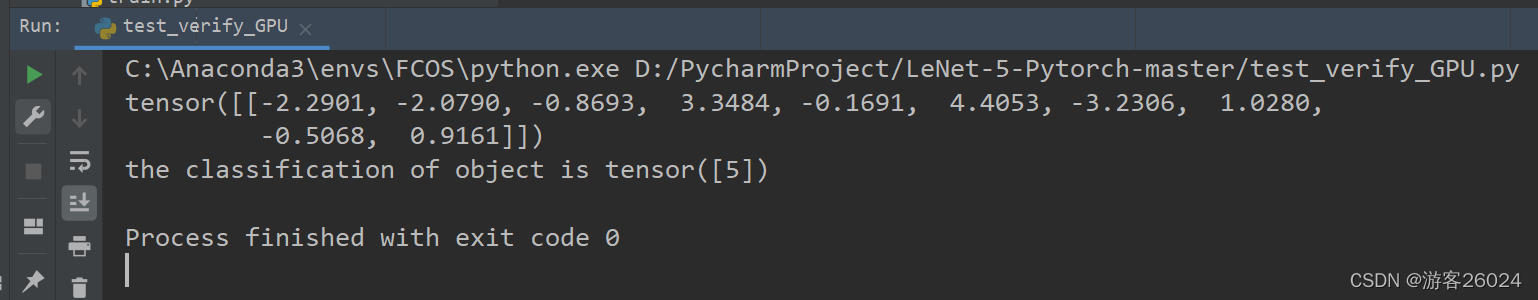
output = model(img)
print(output)
cls = output.argmax(1)
print("the classification of object is {}".format(cls))
其验证的图像为下图
Its verified image is as follows

(run) python test_verify_GPU.py
 成功!
成功!
上一章 18.初识Pytorch之完整的模型套路-合在一个.py文件中 Complete model routine - in one .py file
下一章 20.初识Pytorch使用cuda对模型进行训练和测试或使用cuda对模型进行训练再用cpu测试 Use cuda to train and test the model or use cuda to train the model and then test with cpu

GitCode 天启AI是一款由 GitCode 团队打造的智能助手,基于先进的LLM(大语言模型)与多智能体 Agent 技术构建,致力于为用户提供高效、智能、多模态的创作与开发支持。它不仅支持自然语言对话,还具备处理文件、生成 PPT、撰写分析报告、开发 Web 应用等多项能力,真正做到“一句话,让 Al帮你完成复杂任务”。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)